FDA Approves Paradise Renal Denervation System for Hypertension
The FDA has approved the Paradise Ultrasound Renal Denervation system for treating hypertension. The approval was based on positive reviews by the FDA's Circulatory Systems Device panel. Data from the RADIANCE program and trials supported the approval. Renal denervation is an adjunctive treatment option for hypertension control when lifestyle changes and medication are insufficient. The system delivers ultrasound energy to denervate sympathetic nerves around renal arteries, reducing hypertension. The Paradise system offers significant blood pressure reductions and is beneficial for patients with resistant or mild to moderate hypertension.
Összefoglaló testreszabása
Átírás mesterséges intelligenciával
Hivatkozások generálása
Forrás fordítása
Egy másik nyelvre
Gondolattérkép létrehozása
a forrásanyagból
Forrás megtekintése
www.medscape.com
FDA OKs Paradise Renal Denervation System for Hypertension
Főbb Kivonatok
by Susan Jeffre... : www.medscape.com 11-08-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/998237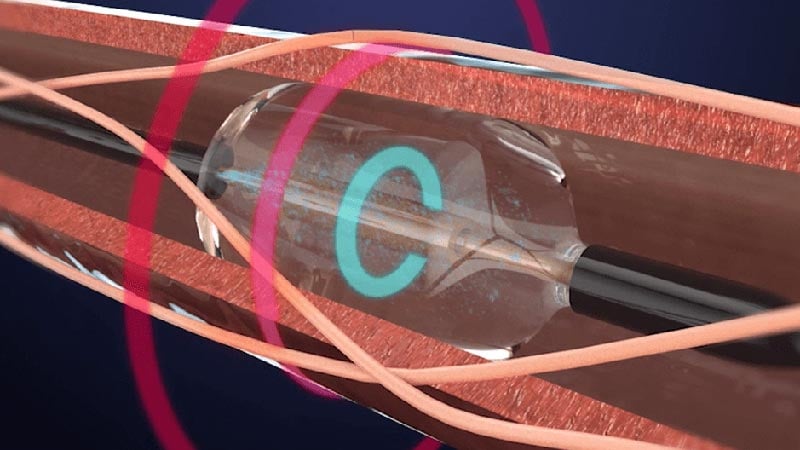
Mélyebb kérdések
