Główne pojęcia
The importance of a One Health approach in Italy to combat zoonotic diseases and protect public health.
Streszczenie
Introduction
- One Health approach emphasized at Welfair healthcare governance fair in Rome.
- Link between human and animal health crucial, especially during pandemics.
Climate-Related Risks
- Global warming impacting the distribution of disease-carrying animal species.
- Expansion of tick and mosquito habitats in Italy due to rising temperatures.
Vets and General Practitioners
- Collaboration between veterinarians and general practitioners essential.
- Challenges in regional healthcare services due to lack of resources.
- Surveillance and response plan for West Nile virus coordinated by Italian National Institute of Health.
Dostosuj podsumowanie
Przepisz z AI
Generuj cytaty
Przetłumacz źródło
Na inny język
Generuj mapę myśli
z treści źródłowej
Odwiedź źródło
www.medscape.com
Italy Considers a One-Health Approach to Zoonotic Diseases
Statystyki
"Monitoring and safeguarding the health of livestock, pets, and wildlife serves to protect human health by controlling and battling against zoonotic diseases."
"Ticks can transmit Rickettsia and meningoencephalitis, and the prevalence of those that can transmit at least one of these diseases is raised in some regions of Italy."
"Veterinary services produce informational material for doctors, providing updates on specific risks in their regions."
Cytaty
"Monitoring and safeguarding the health of livestock, pets, and even wildlife serves not only to prevent financial losses but also to protect human health by controlling and battling against zoonotic diseases." - Antonio Sorice
"Ticks can transmit Rickettsia and meningoencephalitis, and the prevalence of those that can transmit at least one of these diseases is raised in some regions of Italy." - Antonio Sorice
Kluczowe wnioski z
by Cristina Mar... o www.medscape.com 11-08-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/998238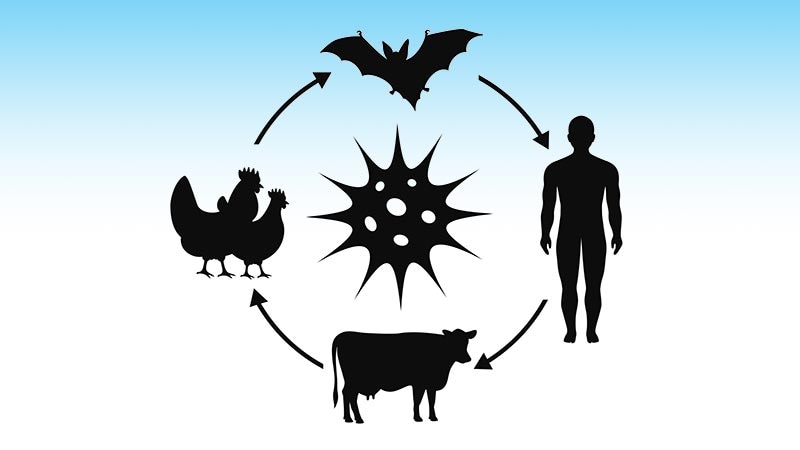
Głębsze pytania
How can other countries adopt a One Health approach to combat zoonotic diseases?
To adopt a One Health approach, other countries can start by recognizing the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. This involves establishing collaborative frameworks between human health professionals, veterinarians, and environmental scientists to monitor and address zoonotic diseases effectively. Countries can create national policies that promote interdisciplinary cooperation, allocate resources for joint surveillance and research efforts, and implement educational programs to raise awareness about the importance of this approach. By fostering partnerships between different sectors and sharing information and expertise, countries can enhance their capacity to prevent, detect, and respond to zoonotic diseases.
What are the potential challenges in implementing a collaborative system between veterinarians and general practitioners?
One of the main challenges in implementing a collaborative system between veterinarians and general practitioners is the lack of communication and coordination between the two groups. Veterinarians and general practitioners often work in separate healthcare systems with different priorities and practices, making it difficult to establish effective partnerships. Additionally, there may be differences in knowledge and understanding of zoonotic diseases, which can hinder collaboration. Resource constraints, such as limited funding and personnel, can also pose challenges to building and sustaining a collaborative system. Overcoming these barriers requires investment in training programs, communication channels, and mutual respect between veterinarians and general practitioners to foster a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility for public health.
How can public awareness and education play a role in preventing the spread of zoonotic diseases?
Public awareness and education are crucial in preventing the spread of zoonotic diseases by promoting behaviors that reduce the risk of transmission. Through targeted campaigns, informational materials, and community outreach initiatives, the public can be informed about the importance of vaccination, proper hygiene practices, and avoiding contact with potentially infected animals. By raising awareness about the signs and symptoms of zoonotic diseases, individuals can seek timely medical attention and prevent further spread. Education efforts can also focus on the ecological factors contributing to disease transmission, such as climate change and habitat destruction, empowering communities to take action to protect themselves and the environment. Ultimately, public awareness and education serve as key components in a comprehensive strategy to mitigate the impact of zoonotic diseases on human and animal health.
0
