Dopaminergic Neuronal Activity-Regulated Myelin Plasticity is Essential for Opioid Reward Processing
المفاهيم الأساسية
Dopaminergic neuronal activity-regulated myelin plasticity in the ventral tegmental area is a key modulator of dopaminergic circuit function and a critical mechanism underlying opioid reward learning.
الملخص
The article explores the role of myelin plasticity in dopaminergic circuitry and reward learning. It demonstrates that dopaminergic neuronal activity-regulated myelin plasticity in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) is a key modulator of dopaminergic circuit function and opioid reward.
The key findings are:
- Oligodendroglial lineage cells respond to dopaminergic neuronal activity evoked by optogenetic stimulation, optogenetic inhibition of GABAergic neurons, or administration of morphine.
- These oligodendroglial changes are selective to the VTA and not observed along the axonal projections in the medial forebrain bundle or within the target nucleus accumbens.
- Genetic blockade of oligodendrogenesis dampens dopamine release dynamics in the nucleus accumbens and impairs behavioral conditioning to morphine.
These findings underscore the critical role of oligodendrogenesis in reward learning and identify dopaminergic neuronal activity-regulated myelin plasticity in the VTA as an important circuit modification required for opioid reward.
تخصيص الملخص
إعادة الكتابة بالذكاء الاصطناعي
إنشاء الاستشهادات
ترجمة المصدر
إلى لغة أخرى
إنشاء خريطة ذهنية
من محتوى المصدر
زيارة المصدر
www.nature.com
Myelin plasticity in the ventral tegmental area is required for opioid reward - Nature
الإحصائيات
Drugs of abuse induce long-lasting changes in synaptic transmission and neural circuit function that underlie substance-use disorders.
Activity-regulated changes in myelin can tune circuit function and influence cognitive behavior.
اقتباسات
"Dopaminergic neuronal activity-regulated myelin plasticity is a key modulator of dopaminergic circuit function and opioid reward."
"Genetic blockade of oligodendrogenesis dampens dopamine release dynamics in nucleus accumbens and impairs behavioural conditioning to morphine."
الرؤى الأساسية المستخلصة من
by Belg... في www.nature.com 06-05-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07525-7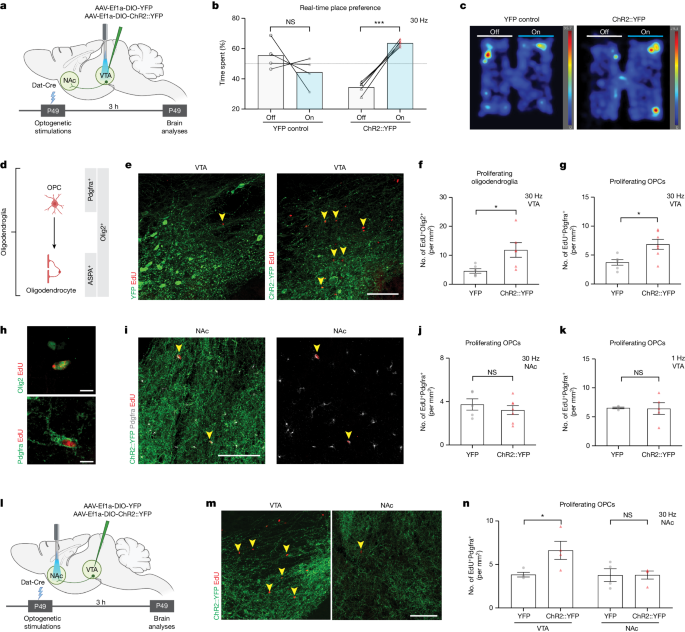
استفسارات أعمق
How do the activity-regulated changes in myelin plasticity in the VTA specifically modulate dopaminergic circuit function and reward processing?
The activity-regulated changes in myelin plasticity in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) play a crucial role in modulating dopaminergic circuit function and reward processing. Oligodendroglial lineage cells within the VTA respond to dopaminergic neuronal activity triggered by various stimuli such as optogenetic stimulation of dopaminergic neurons, optogenetic inhibition of GABAergic neurons, or administration of morphine. These changes in myelin plasticity are localized within the VTA and not along the axonal projections in the medial forebrain bundle or the target nucleus accumbens. By regulating myelin plasticity in the VTA, the dynamics of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens are influenced, impacting behavioral conditioning to opioids like morphine. Therefore, the activity-regulated changes in myelin plasticity in the VTA directly modulate dopaminergic circuit function and reward processing, highlighting the significance of oligodendrogenesis in these processes.
What are the potential therapeutic implications of targeting myelin plasticity in the VTA for the treatment of opioid use disorders?
Targeting myelin plasticity in the VTA for the treatment of opioid use disorders holds significant therapeutic implications. By understanding the role of oligodendroglial lineage cells in response to dopaminergic neuronal activity, interventions can be developed to modulate myelin plasticity in the VTA. Genetic blockade of oligodendrogenesis has been shown to dampen dopamine release dynamics in the nucleus accumbens and impair behavioral conditioning to opioids. Therefore, therapies aimed at enhancing oligodendrogenesis or promoting favorable myelin changes in the VTA could potentially mitigate the rewarding effects of opioids and reduce the risk of substance use disorders. This approach could offer a novel and targeted strategy for the treatment of opioid addiction by addressing the neural circuitry involved in reward processing.
What other brain regions or neural circuits may exhibit similar activity-dependent myelin plasticity, and how might this contribute to various cognitive and behavioral processes?
Activity-dependent myelin plasticity may not be limited to the VTA and could potentially occur in other brain regions or neural circuits. Regions such as the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, or amygdala, which are involved in cognitive and emotional processing, may also exhibit similar mechanisms of myelin plasticity in response to neuronal activity. Changes in myelin sheath thickness or oligodendrocyte function in these regions could impact information processing, learning, memory, and emotional regulation. For example, alterations in myelin plasticity in the prefrontal cortex may influence executive functions and decision-making, while changes in the hippocampus could affect memory formation and retrieval. Therefore, activity-dependent myelin plasticity in various brain regions contributes to a wide range of cognitive and behavioral processes, highlighting the importance of understanding these mechanisms in the context of brain function and dysfunction.
0
