Kernkonzepte
The authors argue that synchronized neuronal activity plays a crucial role in driving waste fluid flow in the brain through the glymphatic system.
Zusammenfassung
The brain's intricate network of neurons generates movement, thought, and behavior through electrical activity. This activity also produces waste that is cleared by the glymphatic system, a unique waste-clearance network in the brain. Jiang-Xie et al. and Murdock et al. present evidence showing how neuronal activation can enhance waste clearance from the brain.
Synchronized neuronal activity drives waste fluid flow
Statistiken
The brain's fluid is filled with waste due to neuronal activity.
The glymphatic system accelerates waste clearance from the brain.
Zitate
"Neuronal activation can accelerate glymphatic waste clearance from the brain."
Wichtige Erkenntnisse aus
by Lauren Habli... um www.nature.com 02-28-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-00422-z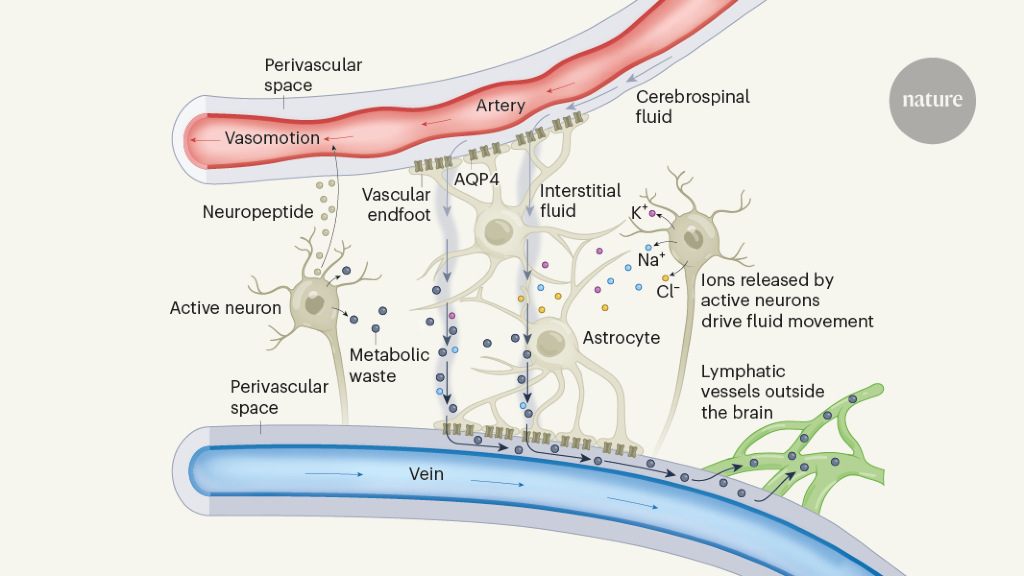
Tiefere Fragen
How does the lack of a lymphatic system in the brain impact waste clearance processes
The lack of a lymphatic system in the brain significantly impacts waste clearance processes. In other parts of the body, the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in removing waste and toxins from tissues. However, since the brain does not have a direct connection to this system, it relies on alternative mechanisms for waste disposal. The glymphatic system, which consists of perivascular spaces alongside blood vessels, serves as the brain's equivalent to the lymphatic system. This network facilitates the clearance of metabolic waste products and toxins from the central nervous system.
What implications does this research have for understanding neurological disorders related to waste accumulation in the brain
The research indicating that synchronized neuronal activity can accelerate glymphatic waste clearance has profound implications for understanding neurological disorders associated with waste accumulation in the brain. Conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders are characterized by an accumulation of toxic proteins and metabolic by-products in the brain tissue. By elucidating how neuronal activation influences waste removal through the glymphatic system, researchers may uncover new therapeutic targets for these diseases. Enhancing glymphatic function could potentially help mitigate or prevent pathological buildup linked to these neurological conditions.
How can advancements in studying neuronal activity and waste disposal benefit other areas of neuroscience research
Advancements in studying neuronal activity and waste disposal hold significant promise for various areas of neuroscience research beyond understanding neurological disorders specifically related to waste accumulation in the brain. By exploring how synchronized neuronal activity affects glymphatic clearance processes, scientists can gain insights into broader aspects of brain health and function. This research could lead to a better comprehension of cognitive processes, memory formation, sleep regulation, and overall brain homeostasis.
Moreover, advancements in this field may also inform studies on traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), stroke recovery mechanisms, and age-related cognitive decline. Understanding how neural activity influences waste removal pathways could offer novel strategies for promoting neuroregeneration after injury or enhancing cognitive resilience during aging processes.
0
