Response to Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab in Desmoplastic Melanoma
Concepts de base
Desmoplastic melanoma patients show a remarkable response to neoadjuvant pembrolizumab, avoiding postoperative radiation therapy.
Résumé
The study focused on the response of desmoplastic melanoma patients to neoadjuvant pembrolizumab, highlighting impressive results and potential benefits for this patient population.
Key Highlights:
- Study on neoadjuvant use of anti-PD1 immunotherapy in desmoplastic melanoma.
- Postexcision complete response rates were significantly higher compared to other advanced melanomas.
- 81% of patients had no residual viable tumor at the primary site.
- Only one patient required radiation therapy post-surgery.
- Encouraging results for both 'mixed' and 'pure' desmoplastic subtypes.
- Desmoplastic melanoma typically requires radical resection due to its invasiveness.
- Pathologic complete response seen in 55% of patients.
- High sensitivity of desmoplastic melanoma to neoadjuvant treatment.
- Potential survival benefits yet to be determined.
- Immunotherapy mechanisms offer promising outcomes for long-term responses.
Personnaliser le résumé
Réécrire avec l'IA
Générer des citations
Traduire la source
Vers une autre langue
Générer une carte mentale
à partir du contenu source
Voir la source
www.medscape.com
'Astounding' Response to Neoadjuvant Desmoplastic Melanoma Tx
Stats
"No residual viable tumor was found at the primary site in an astounding 81% of these patients," - Vernon K. Sondak, MD
"The fact that our pathologic complete response was much higher [55%] — overall twice what we might expect — is in keeping with our expectation going into the study that desmoplastic melanomas would be more sensitive to neoadjuvant pembrolizumab," - Vernon K. Sondak, MD
Citations
"I am unaware of any other therapy that produces such a high response rate in the neoadjuvant setting in this group of patients." - Mary Sue Brady, MD
"Indeed, one of the real advantages of immunotherapy is that if you can stimulate the body's immune system to reject a tumor, the immune cells remain on guard against recurrence for many years thereafter." - Vernon K. Sondak, MD
Idées clés tirées de
by Nancy A. Mel... à www.medscape.com 03-29-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/990229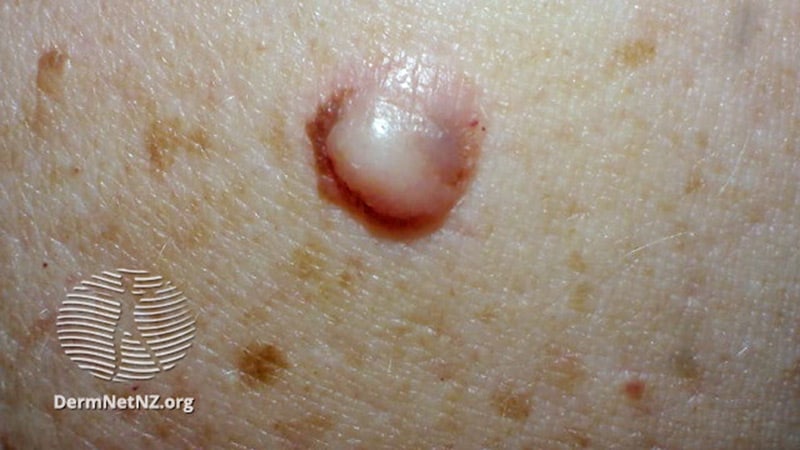
Questions plus approfondies
How can the high response rates observed in this study impact the standard treatment protocols for desmoplastic melanoma patients?
The high response rates observed in this study can have a significant impact on the standard treatment protocols for desmoplastic melanoma patients. The study showed that neoadjuvant pembrolizumab resulted in an astounding 81% of patients having no residual viable tumor at the primary site. This is a much higher response rate compared to other advanced melanomas. As a result, the need for postoperative radiation therapy was greatly reduced, with only one out of 21 patients requiring radiation after surgery. This suggests that neoadjuvant immunotherapy could potentially replace or reduce the need for postoperative radiation in desmoplastic melanoma patients. These findings may lead to a shift in treatment guidelines towards incorporating neoadjuvant immunotherapy as a standard part of the treatment protocol for desmoplastic melanoma.
What are the potential implications of the study results on the future of neoadjuvant therapies in melanoma treatment?
The study results have significant implications for the future of neoadjuvant therapies in melanoma treatment. The high response rates seen in desmoplastic melanoma patients treated with neoadjuvant pembrolizumab suggest that this approach could be highly effective in this subtype of melanoma. The study demonstrated a pathologic complete response rate of 55%, which is much higher than what is typically seen in other melanoma types. This indicates that neoadjuvant immunotherapy may be particularly beneficial for desmoplastic melanoma patients. The success of this study may pave the way for further research and clinical trials exploring the use of neoadjuvant immunotherapy in other melanoma subtypes and stages. It could also lead to the development of new treatment guidelines that prioritize neoadjuvant therapies as a standard part of melanoma treatment protocols.
How can the aging population trend influence the incidence and management of desmoplastic melanoma in the coming years?
The aging population trend is expected to have a significant influence on the incidence and management of desmoplastic melanoma in the coming years. Desmoplastic melanoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically on the head or neck. With the aging population expanding rapidly, clinicians can anticipate an increase in the rates of this type of melanoma. This demographic shift may lead to a higher number of desmoplastic melanoma cases being diagnosed and treated. As older patients are often more vulnerable to the side effects of aggressive treatments like surgery and radiation, the findings of this study, which suggest that neoadjuvant immunotherapy can be highly effective with fewer side effects, could have a profound impact on the management of desmoplastic melanoma in the aging population. Clinicians may increasingly turn to neoadjuvant therapies as a safer and more effective treatment option for older patients with desmoplastic melanoma.
0
