Synthetic Opioid Overdoses: A Compound with Potential to Revolutionize Overdose Treatment
Alapfogalmak
A newly discovered compound could provide a novel strategy to save lives of people who have overdosed on synthetic opioids like fentanyl.
Kivonat
The content discusses the devastating impact of the opioid crisis in the United States, where synthetic opioids like fentanyl have claimed tens of thousands of lives. Despite increased public awareness and research efforts, opioid overdoses continue to be a major public health issue, with an estimated 74,702 deaths from synthetic opioid overdoses in 2023 alone.
The article then introduces a new compound described and characterized by O'Brien et al. in a study published in Nature. This compound could offer a different strategy for saving the lives of people who have overdosed on opioids, potentially revolutionizing the approach to this critical public health problem.
Opioid crisis: compound opens up potential strategy to tackle overdoses
Statisztikák
In 2023, an estimated 74,702 people died after overdosing on synthetic opioids, which was 70% of the total number of drug overdose deaths that year.
Idézetek
"The illegal use of synthetic opioids such as fentanyl and its analogues has killed tens of thousands of people and wreaked devastation on families across the United States."
"Indeed, in 2017, the White House declared the opioid crisis to be a public-health emergency."
Főbb Kivonatok
by Catherine M.... : www.nature.com 07-03-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-02133-x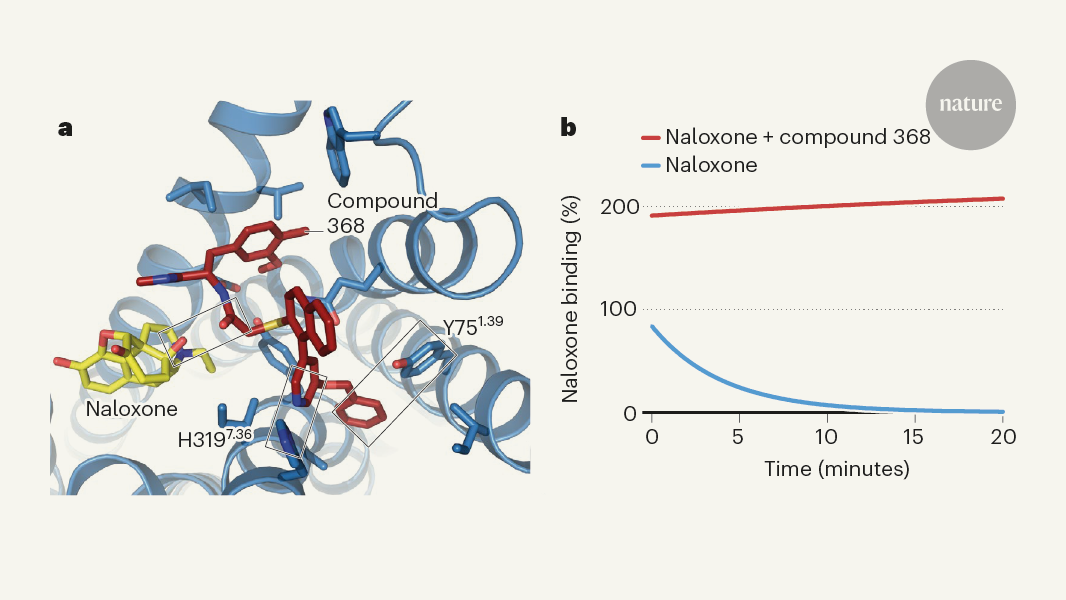
Mélyebb kérdések
What are the key mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications of the newly discovered compound?
The newly discovered compound described by O’Brien et al. in Nature offers a unique mechanism of action in tackling opioid overdoses. This compound works by targeting specific receptors in the brain that are involved in the respiratory depression caused by opioid overdose. By binding to these receptors, the compound can reverse the effects of the opioids and restore normal breathing patterns, potentially saving the lives of individuals who have overdosed. Additionally, this compound has shown promise in reducing the addictive properties of opioids, making it a potential candidate for addiction treatment as well. The therapeutic applications of this compound extend beyond just reversing overdoses to potentially helping individuals break free from opioid dependence.
What are the potential challenges and limitations in developing and implementing this new approach to address the opioid crisis?
While the newly discovered compound presents a promising strategy for addressing the opioid crisis, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be considered. One major challenge is the need for extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the compound in real-world settings. Additionally, regulatory hurdles and approval processes can delay the implementation of this new approach. Another limitation is the potential for resistance or side effects to develop over time, which could impact the long-term effectiveness of the compound. Moreover, the cost of production and distribution of the compound may pose challenges in making it accessible to those who need it the most, especially in underserved communities.
How can this research be leveraged to drive broader innovations in the field of addiction treatment and harm reduction strategies?
The research on the newly discovered compound can serve as a catalyst for driving broader innovations in addiction treatment and harm reduction strategies. By understanding the mechanisms of action of this compound, researchers can develop new drugs that target specific pathways involved in addiction and overdose. This could lead to the discovery of more effective and targeted treatments for opioid dependence. Furthermore, the success of this research can inspire funding agencies and pharmaceutical companies to invest in similar research efforts, leading to a wave of innovation in the field. Additionally, the findings from this research can inform public health policies and interventions aimed at reducing the harm caused by opioids, ultimately saving more lives and improving the well-being of individuals affected by the opioid crisis.
0
