Core Concepts
Bees and chimpanzees exhibit skills that hint at the potential for cumulative culture, shedding light on the capacity of animals to learn from others. The authors explore how social learning plays a crucial role in the development of skills and technologies among different species.
Abstract
Humans' ability to innovate and improve skills through cumulative culture is a unique trait. Recent studies on bees and chimpanzees suggest that these animals also possess the capacity for social learning, which could be essential for achieving cumulative culture. This highlights the importance of observing and understanding animal behavior to gain insights into our own evolutionary processes.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
Bees and chimpanzees learn from others what they cannot learn alone
Stats
Studies by Bridges et al.1 in Nature
van Leeuwen et al.2 in Nature Human Behaviour
Quotes
Key Insights Distilled From
by Alex Thornto... at www.nature.com 03-06-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-00427-8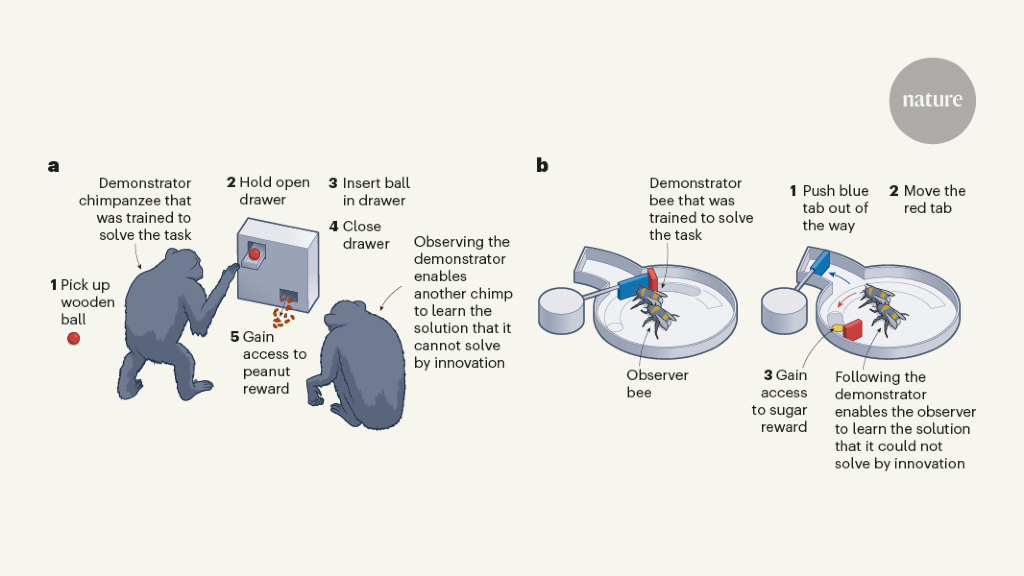
Deeper Inquiries
How does social learning in animals compare to human cultural evolution?
Social learning in animals involves the transmission of knowledge and skills from one individual to another within a species. While this form of learning is present in various animal species, including bees and chimpanzees as mentioned in the context, it differs from human cultural evolution in several key ways.
Firstly, human cultural evolution involves the accumulation and refinement of knowledge and practices over generations through a process known as cumulative culture. This means that innovations are not only passed down but also built upon by subsequent generations, leading to continuous improvement and development. In contrast, social learning in animals typically focuses on immediate survival needs or behaviors without necessarily leading to long-term cumulative changes.
Secondly, humans have developed complex symbolic communication systems such as language that enable the transfer of abstract concepts and ideas across individuals and time periods. This linguistic ability plays a crucial role in shaping our cultural evolution by allowing for more sophisticated forms of teaching, learning, and collaboration compared to most animal species.
Overall, while both social learning in animals and human cultural evolution involve the transmission of information between individuals within a group or population, the latter is characterized by its capacity for cumulative culture driven by advanced cognitive abilities like language.
What implications does the potential for cumulative culture in animals have for conservation efforts?
The recognition of potential cumulative culture among certain animal species has significant implications for conservation efforts aimed at protecting biodiversity and preserving ecosystems. If animals possess the ability to develop increasingly sophisticated behaviors through social learning mechanisms similar to humans' cumulative culture, this suggests that they may be more adaptable than previously thought.
By understanding how animals learn from each other and potentially build upon their collective knowledge over time, conservationists can tailor strategies that leverage these natural capacities towards promoting resilience against environmental challenges such as habitat loss or climate change. For instance, interventions could focus on facilitating opportunities for knowledge transfer within populations or enhancing access to resources that support innovative behaviors.
Furthermore, acknowledging the presence of cumulative culture in animals underscores their intrinsic value beyond mere genetic diversity. It highlights their capacity for dynamic responses to changing conditions based on shared experiences—a quality that can inform more holistic approaches to conservation management grounded in fostering adaptive capacities among wildlife populations.
How can studying animal behavior contribute to advancements in human society?
Studying animal behavior offers valuable insights into fundamental principles underlying cognition, communication patterns,
and social dynamics—knowledge that can be applied towards addressing various challenges faced by human society.
For example:
Medical Research: Observing how certain animal species navigate complex environments or exhibit problem-solving skills can inspire new approaches
medical research related tasks requiring spatial awareness or critical thinking.
Technology Development: By studying how animals communicate using non-verbal cues or signals,
researchers gain inspiration developing technologies improve interpersonal interactions efficiency.
3 .Environmental Conservation: Understanding migratory patterns behavioral adaptations different wildlife species informs
effective strategies conserving habitats mitigating threats posed anthropogenic activities climate change
In essence ,studying animal behavior serves as an interdisciplinary bridge connecting biological sciences with fields ranging psychology anthropology sociology engineering Ultimately ,the lessons learned from observing nature's diverse inhabitants hold promise driving innovation improving societal well-being
0
