Unveiling the Uncertainty in Biodiversity Change Analysis
The content discusses the challenges faced by biodiversity due to rapid global change. It highlights the signals of biodiversity change from abundance datasets for various species across different scales. The analysis reveals that existing approaches fail to fully consider spatial, temporal, and phylogenetic structures in the data, leading to underestimation of trend uncertainty and misestimation of trend direction. The new statistical framework applied to high-profile biodiversity datasets shows that trends in abundance vanish once these structures are accounted for, emphasizing the lack of knowledge about biodiversity change on vast scales. However, improved local-scale prediction accuracy is achieved by considering these structures, offering hope for estimating biodiversity change at policy-relevant scales and guiding conservation responses.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
Revealing uncertainty in the status of biodiversity change - Nature
Key Insights Distilled From
by T. F. Johnso... at www.nature.com 03-27-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07236-z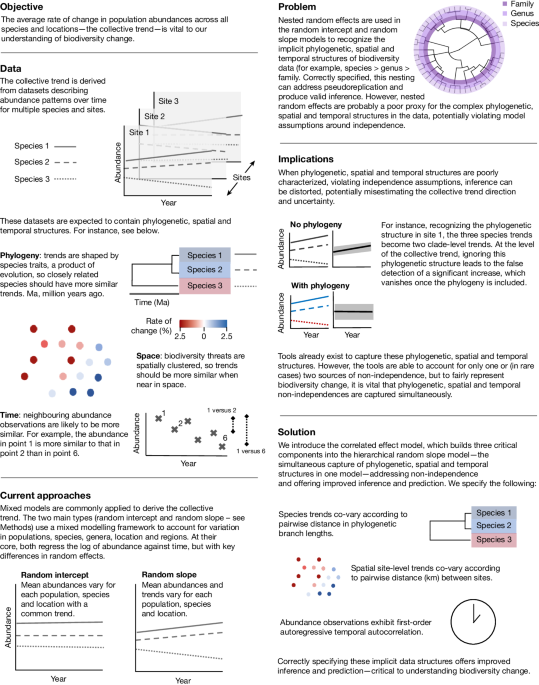
Deeper Inquiries
