Collective Sensing in Electric Fish: Utilizing Conspecific Signals for Enhanced Perception
Core Concepts
The author argues that African weakly electric fish utilize conspecific electrical pulses to enhance their electrolocation range and increase information transmission, presenting a new collective mode of active sensing.
Abstract
African weakly electric fish, like other organisms such as dolphins and bats, possess active sensory systems using self-generated signals to probe the environment. While previous studies focused on minimizing interference from conspecific emissions, this research shows how these fish use the electrical pulses of group members to extend their electrolocation range, discriminate objects, and enhance individual perception through collective sensing strategies.
Collective sensing in electric fish - Nature
Stats
Studies show that multiple spatially distributed emitters and receivers can greatly enhance environmental sensing.
The African weakly electric fish Gnathonemus petersii utilizes conspecific electrical pulses to extend its electrolocation range and increase information transmission.
Quotes
Key Insights Distilled From
by Federico Ped... at www.nature.com 03-06-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07157-x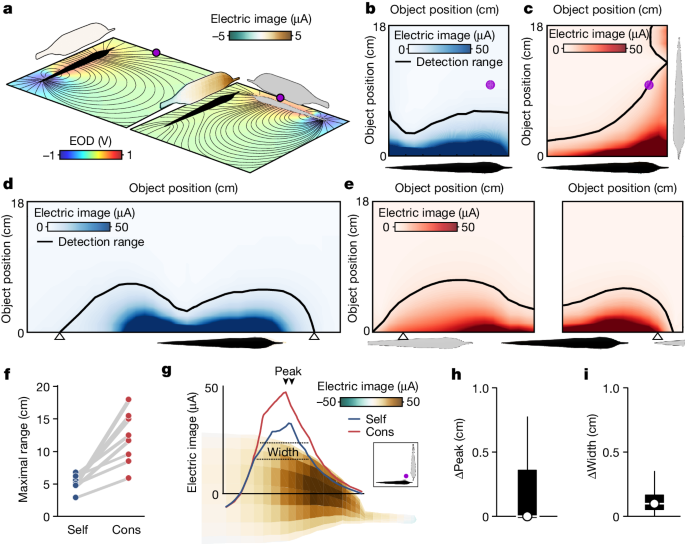
Deeper Inquiries
How does the collective sensing strategy observed in electric fish compare to other species with active sensory systems
The collective sensing strategy observed in electric fish, specifically the African weakly electric fish Gnathonemus petersii, differs from other species with active sensory systems in its utilization of conspecific electrical pulses to enhance electrolocation range and object discrimination. While species like dolphins and bats rely on self-generated signals for echolocation or navigation, the electric fish takes advantage of nearby group members' energy emissions to improve individual perception. This unique approach showcases a collaborative mode of active sensing where multiple spatially distributed emitters and receivers work together to enhance environmental sensing.
What are the potential implications of understanding and replicating this collective sensing mechanism in technological applications
Understanding and replicating the collective sensing mechanism observed in electric fish could have significant implications for technological applications, particularly in fields such as underwater exploration and surveillance. By mimicking how these fish utilize conspecific electrical pulses to extend their electrolocation range and increase information transmission, engineers could develop more efficient multistatic radar or sonar systems. These technologies could greatly enhance our ability to detect objects underwater, navigate complex environments, and potentially even improve communication networks by leveraging collective sensing strategies inspired by nature.
How might studying the behavior of electric fish contribute to advancements in underwater exploration technologies
Studying the behavior of electric fish can contribute significantly to advancements in underwater exploration technologies by providing insights into novel sensory mechanisms that can be applied in engineering solutions. By understanding how these fish use electrical emissions from nearby group members to enhance their perception abilities, researchers can design innovative sensor arrays for underwater vehicles or autonomous robots. These bio-inspired technologies could revolutionize underwater exploration by improving detection capabilities, increasing data transmission efficiency, and enabling more precise mapping of aquatic environments based on principles derived from collective sensing strategies exhibited by electric fish like Gnathonemus petersii.
0
