Core Concepts
Dermatologist shares insights on diagnosing and managing Spitz nevi, emphasizing the limitations of dermoscopy.
Abstract
The content discusses the challenges in diagnosing and managing Spitz nevi, highlighting the importance of not solely relying on dermoscopy. Key points include:
Classic signs of Spitz nevi on dermoscopy.
Results from a retrospective study questioning the reliability of dermoscopy.
Importance of biopsy in diagnosing Spitzoid lesions in children.
Impact of biopsy method on residual lesion presence.
Parameters for diagnosing Spitzoid tumors under the microscope.
Treatment recommendations for children with biopsy-proven Spitz nevi.
Considerations for excision and observation based on biopsy results.
Lack of outcomes data supporting sentinel lymph node biopsy for atypical Spitz tumors.
Spitz Nevi: An Expert Shares Tips for Diagnosis, Management
Stats
"On histology, 86.7% were diagnosed as benign Spitz nevi, and 13.3% were diagnosed as melanoma."
"The presence of residual lesion in the re-excision specimen was significantly higher when the initial biopsy was done by punch biopsy (90.9%) when compared with shave biopsy (48.9%) and formal excision (62.5%; P < .05)."
Quotes
"I respect the dermoscopy criteria, but I don't rely solely on it."
"Even today, it remains controversial whether you should do a shave or punch biopsy."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Doug Brunk at www.medscape.com 02-09-2024
https://www.medscape.com/s/viewarticle/spitz-nevi-expert-shares-tips-diagnosis-management-2024a10002vn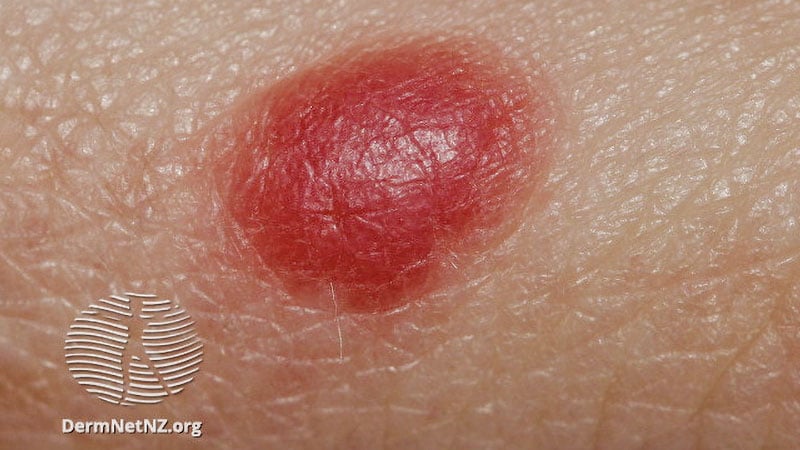
Deeper Inquiries
How can advancements in imaging technology improve the accuracy of diagnosing Spitz nevi?
Advancements in imaging technology, such as dermoscopy, confocal microscopy, and reflectance confocal microscopy, can significantly enhance the accuracy of diagnosing Spitz nevi. These technologies allow for non-invasive visualization of skin lesions at a cellular level, providing detailed information about the structure and morphology of the lesion. Dermoscopy, for example, enables dermatologists to identify specific patterns and features characteristic of Spitz nevi, aiding in differentiation from other skin lesions. Confocal microscopy offers real-time imaging of skin layers, helping in the assessment of cellular atypia and architectural disarray. By incorporating these imaging modalities into the diagnostic process, healthcare providers can improve diagnostic accuracy, leading to better management decisions for patients with Spitz nevi.
What are the potential drawbacks of overreliance on biopsy in the diagnosis of skin lesions?
While biopsy is a crucial tool in the diagnosis of skin lesions, overreliance on this procedure can have potential drawbacks. One significant drawback is the risk of sampling error, where the biopsy may not capture the entire lesion or miss areas of concern, leading to an inaccurate diagnosis. Additionally, repeated biopsies can result in scarring and cosmetic concerns, especially in visible areas of the body. Overreliance on biopsy may also lead to unnecessary procedures, increasing healthcare costs and patient discomfort. Moreover, in cases of benign lesions like Spitz nevi, aggressive biopsy approaches may result in overtreatment and unnecessary anxiety for patients and their families. Therefore, while biopsy is essential for definitive diagnosis, it should be complemented with clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and interdisciplinary discussions to ensure a comprehensive and accurate diagnostic approach.
How can interdisciplinary collaboration enhance the management of pediatric patients with atypical Spitz tumors?
Interdisciplinary collaboration plays a crucial role in enhancing the management of pediatric patients with atypical Spitz tumors. By involving specialists from various fields such as dermatology, pathology, oncology, and surgery, healthcare providers can benefit from diverse perspectives and expertise in managing complex cases. Pathologists can provide valuable insights into the histological features of atypical Spitz tumors, guiding treatment decisions and prognostic assessments. Oncologists can offer recommendations on systemic therapies and lymph node evaluation, especially in cases of nodal metastases. Surgeons can contribute their expertise in excision techniques and follow-up care for patients undergoing surgical interventions. Through collaborative discussions and multidisciplinary tumor boards, healthcare teams can develop individualized treatment plans that consider the unique needs of pediatric patients with atypical Spitz tumors, leading to improved outcomes and quality of care.
0
