Impact of Climate Change on Bee Populations
Core Concepts
Climate change poses a significant threat to bee populations, with extreme climate conditions directly impacting their long-term stability and leading to potential declines in various species.
Abstract
The content highlights the growing threat of climate change on bee populations, with research indicating that climate extremes are contributing to declines in bees, butterflies, flies, and moths. While previous studies have shown correlational evidence, new research is filling the gap by providing direct physiological effects of extreme climate conditions on bees' population stability. The study by Kazenel et al. in Nature demonstrates these effects, while Ghisbain et al. predict significant declines in bumblebees, including species currently listed as 'least concern' by the IUCN.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
Climate change predicted to exacerbate declines in bee populations
Stats
Research suggests climate extremes contribute to declines in bees, butterflies, flies, and moths.
Kazenel et al. provide evidence of direct physiological effects of extreme climate conditions on bee populations.
Ghisbain et al. predict declines in bumblebees, including species listed as 'least concern' by the IUCN.
Quotes
"Climate change is rapidly becoming a prominent threat, contributing to declines in bees, butterflies, flies, and moths."
"New research is filling the gap by providing direct evidence of the physiological effects of extreme climate conditions on bee populations."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Nicole E. Mi... at www.nature.com 03-27-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-00681-w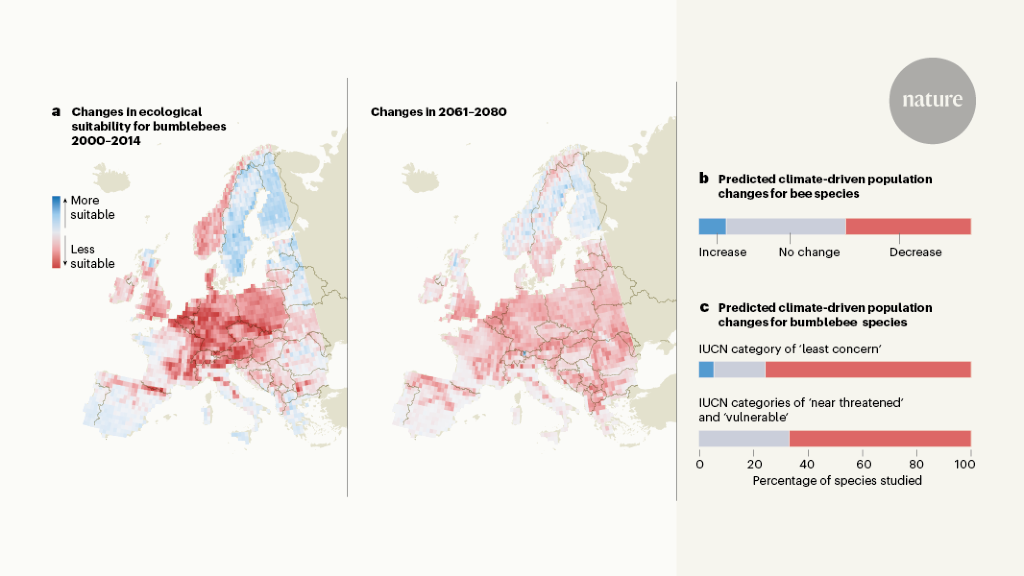
Deeper Inquiries
How can conservation efforts adapt to mitigate the impact of climate change on bee populations?
Conservation efforts can adapt to mitigate the impact of climate change on bee populations by implementing various strategies. These include creating and preserving habitats that are resilient to climate change, such as diverse floral resources and nesting sites. Additionally, promoting sustainable land management practices, reducing pesticide use, and enhancing genetic diversity within bee populations can help bees adapt to changing environmental conditions. Conservationists can also engage in monitoring and research to better understand the specific effects of climate change on bee species and develop targeted conservation plans accordingly.
What are the potential implications of declining bee populations on ecosystems and agriculture?
The declining bee populations can have significant implications on ecosystems and agriculture. Bees play a crucial role in pollinating a wide variety of plants, including many crops that are essential for food production. A decline in bee populations can lead to reduced crop yields, decreased biodiversity, and disruptions in ecosystem functioning. This can have cascading effects on other wildlife species that depend on the plants that bees pollinate. In agriculture, the loss of bees can result in lower crop productivity, increased production costs, and potential food shortages. Overall, declining bee populations can have far-reaching consequences for both natural ecosystems and human food systems.
How can policymakers address the challenges posed by climate change to ensure the preservation of bee species?
Policymakers can address the challenges posed by climate change to ensure the preservation of bee species by implementing policies that promote habitat conservation, sustainable agriculture, and climate change mitigation. This can include creating protected areas for bees, incentivizing farmers to adopt bee-friendly practices, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow the pace of climate change. Policymakers can also support research and monitoring efforts to better understand the impacts of climate change on bee populations and develop evidence-based conservation strategies. Collaboration between policymakers, scientists, conservationists, and stakeholders is essential to effectively address the complex challenges posed by climate change and ensure the long-term preservation of bee species.
0
