Gut Microbiome Role in Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
Core Concepts
Gut microbiome differences in treatment-resistant schizophrenia may be influenced by clozapine treatment.
Abstract
The study explores the impact of gut microbiome differences in individuals with treatment-resistant schizophrenia, particularly those taking clozapine. Key points include:
- Gut microbiome variations in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
- Potential influence of clozapine on gut microbiome.
- Importance of considering microbiome in treatment strategies.
- Associations between gut microbiome and treatment resistance.
- Expert opinions on the study's implications and limitations.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.medscape.com
Gut Signature for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia?
Stats
"Up to 30% of people with schizophrenia are treatment-resistant and experience persistent symptoms despite two or more antipsychotic treatment trials."
"The investigators observed 'robust' taxonomic and functional microbiome associations with schizophrenia and treatment resistance."
"The microbiome composition of individuals with treatment-responsive schizophrenia was more similar to that of controls without psychiatric diagnoses than to that of individuals with treatment-resistant schizophrenia who were taking clozapine."
Quotes
"Studies are needed to understand the clinical implications of our finding of an altered microbiome among people with treatment-resistant schizophrenia taking clozapine, specifically whether therapeutic strategies for treatment-resistant schizophrenia should consider microbiome adjuvants, including diet, physical activity, and probiotics."
"This line of research is exciting because it has implications for both mechanistic understanding and therapeutics."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Megan Brooks at www.medscape.com 02-07-2024
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/gut-signature-treatment-resistant-schizophrenia-2024a10002op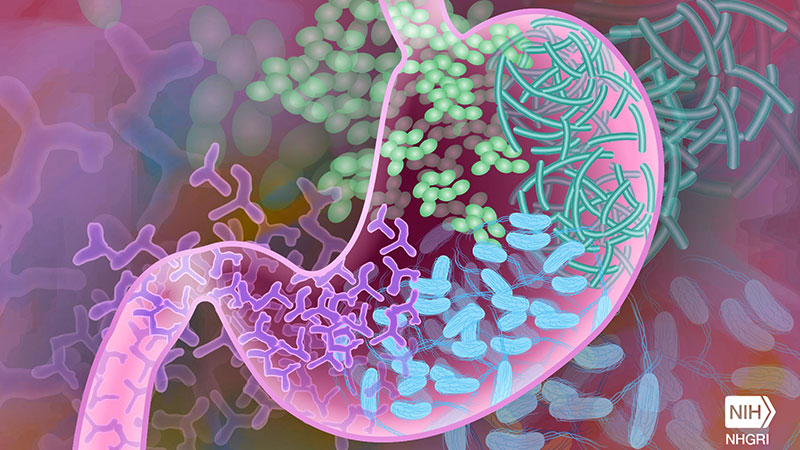
Deeper Inquiries
What other factors beyond gut microbiome could contribute to treatment-resistant schizophrenia?
In addition to gut microbiome differences, several other factors could contribute to treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Genetic predisposition, neuroinflammation, neurotransmitter imbalances, structural brain abnormalities, medication non-adherence, substance abuse, environmental stressors, and social determinants of health are all potential contributors to the development and persistence of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Understanding the complex interplay of these factors is crucial for developing comprehensive treatment strategies for individuals with this challenging condition.
Is there a potential downside to focusing solely on microbiome-based treatments for schizophrenia?
While the gut microbiome shows promise as a potential target for treatment in schizophrenia, focusing solely on microbiome-based treatments may have limitations. Relying exclusively on microbiome interventions could overlook other important aspects of the disorder, such as genetic factors, neural circuitry abnormalities, and psychosocial influences. Additionally, the microbiome is just one piece of the puzzle in the complex etiology of schizophrenia. A holistic approach that integrates microbiome-based treatments with traditional pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, and social support may offer more comprehensive and effective outcomes for individuals with schizophrenia.
How might advancements in microbiome research impact other areas of mental health treatment?
Advancements in microbiome research have the potential to revolutionize various areas of mental health treatment beyond schizophrenia. Studies have linked gut dysbiosis to conditions like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and autism spectrum disorders. By understanding the role of the microbiome in these conditions, researchers may develop novel therapeutic interventions targeting the gut-brain axis. Personalized microbiome-based treatments, including probiotics, prebiotics, dietary modifications, and fecal microbiota transplants, could offer new avenues for managing mental health disorders. Furthermore, microbiome research may lead to the development of biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and treatment response prediction in various mental health conditions, paving the way for precision medicine approaches in psychiatry.
0
