New Marker of Cardiovascular Risk Discovered in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Core Concepts
Dysfunctional monocytes indicate poor cardiovascular prognosis in type 2 diabetes patients.
Abstract
Introduction:
Dysfunctional monocytes linked to cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients.
Research led by Nicolas Venteclef, PhD, from an Inserm institute in Paris.
Quantifying Inflammation:
Type 2 diabetes patients have higher cardiovascular event risks.
Inflammation plays a crucial role in predicting complications.
Focus on quantifying inflammation through monocytes in the blood.
Dysfunctional Monocytes:
Study with three patient cohorts showing higher monocyte levels increase cardiovascular risk.
Molecular analysis reveals specific monocyte subtypes in high-risk patients.
Patients with monocyte count above a threshold have significantly higher cardiovascular event risks.
Future Steps:
Patent filed to protect the discovery.
Plans to develop a sensor for easier monocyte quantification.
Trial with anti-inflammatory drug to prevent complications in diabetics.
New Marker of Cardiovascular Risk Discovered in T2D
Stats
"The higher the number of circulating monocytes, the greater the risk for cardiovascular events."
"Patients with monocyte count above a certain threshold had a five- to seven-times higher risk for cardiovascular events over 10 years."
Quotes
"Predicting these complications in diabetic patients is usually very difficult."
"Our next step is to develop a sensor to quantify monocytes more easily and avoid blood draws."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Anne... at www.medscape.com 02-19-2024
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/new-marker-cardiovascular-risk-discovered-t2d-2024a10003bx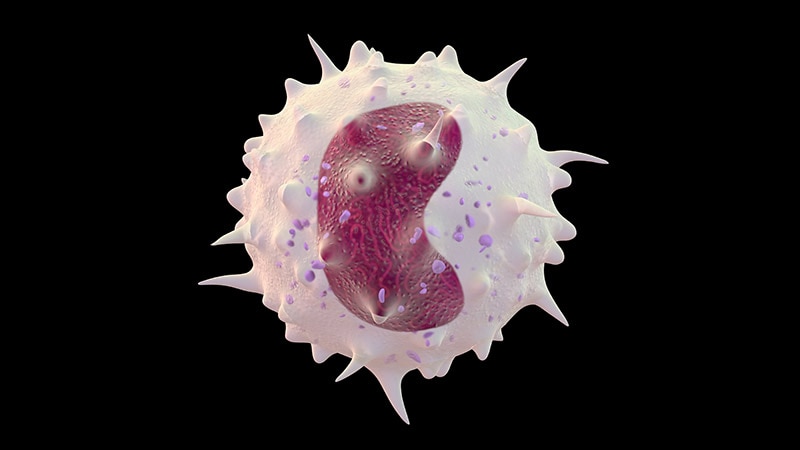
Deeper Inquiries
How can the discovery of dysfunctional monocytes impact the treatment of cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients
The discovery of dysfunctional monocytes in type 2 diabetes patients can significantly impact the treatment of cardiovascular risk. By identifying these dysfunctional monocytes with mitochondrial issues, healthcare providers can better predict cardiovascular events such as heart attacks or strokes in diabetic individuals. This knowledge allows for targeted interventions to address the underlying inflammation associated with these dysfunctional monocytes. For instance, developing specific therapies that target these dysfunctional monocytes could help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications in type 2 diabetes patients. Additionally, the ability to quantify monocyte levels and assess the cardiovascular risk associated with them provides a more personalized approach to managing cardiovascular health in diabetic individuals.
What potential challenges or limitations might arise in using monocyte levels as a marker for cardiovascular risk prediction
Despite the potential benefits of using monocyte levels as a marker for cardiovascular risk prediction in type 2 diabetes patients, several challenges and limitations may arise. One challenge is the need for standardized methods to measure and interpret monocyte levels accurately across different healthcare settings. Variability in measurement techniques or interpretation of results could lead to inconsistencies in predicting cardiovascular risk. Additionally, factors such as comorbidities, medication use, and lifestyle habits may influence monocyte levels, making it challenging to isolate the specific impact of dysfunctional monocytes on cardiovascular risk. Furthermore, the cost and accessibility of testing for monocyte levels could pose limitations in widespread implementation as a predictive marker for cardiovascular events in diabetic patients.
How can advancements in technology and medicine further improve the management of cardiovascular complications in diabetes patients
Advancements in technology and medicine hold great potential to further improve the management of cardiovascular complications in diabetes patients. One key area of advancement is the development of sensors or diagnostic tools that can easily and accurately quantify monocyte levels in the blood. These tools could streamline the process of assessing cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients, enabling healthcare providers to intervene early and effectively. Additionally, advancements in personalized medicine, such as targeted therapies that specifically address dysfunctional monocytes, could revolutionize the treatment of cardiovascular complications in diabetic individuals. Collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and technology experts can lead to innovative solutions that enhance the prevention and management of cardiovascular risks in patients with type 2 diabetes.
0
