The Impact of Misuse of Antifungal Medications on the Rise of Superfungi
Unnecessary or incorrect use of topical antifungal medications is leading to the proliferation of fungal infections like ringworm, making them harder to treat. The study emphasizes the importance of confirming diagnoses through lab testing before prescribing treatments and educating patients on proper usage of antifungal medications. The misuse of antifungals has led to the emergence of resistant strains, posing a significant public health concern. Prescription patterns reveal a high number of antifungal prescriptions, with primary care clinicians being the major prescribers. The study highlights the need for clinicians to confirm diagnoses and avoid unnecessary prescriptions to prevent the development of more resilient fungi.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.medscape.com
Are You Unwittingly Aiding the Rise of Superfungi?
Key Insights Distilled From
by Marcus A. Ba... at www.medscape.com 01-12-2024
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/are-you-unwittingly-aiding-rise-superfungi-2024a10000vy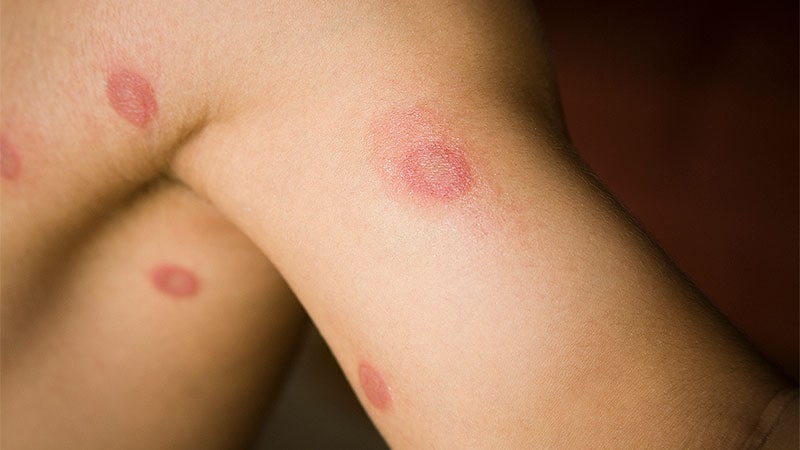
Deeper Inquiries
