Genetic Screening and Zoledronic Acid Treatment for Paget Disease Prevention
Core Concepts
Prophylactic treatment with zoledronic acid in high-risk individuals can prevent Paget disease progression.
Abstract
The study highlights the effectiveness of genetic screening and zoledronic acid treatment in preventing Paget disease progression. Here is a breakdown of the key points:
Introduction:
Zoledronic acid (ZA) can prevent Paget disease of the bone (PDB) in high-risk individuals.
Genetic screening is crucial for individuals with a familial history of PDB.
Disease Overview:
PDB is a chronic skeletal growth disorder affecting millions in the US.
Symptoms may not appear until late stages, leading to irreversible skeletal damage.
Genetic Influence:
Pathogenic variants of SQSTM1 gene play a significant role in PDB.
Early interventions in high-risk individuals may halt disease progression.
Study Details:
Over 1400 individuals with PDB underwent genetic testing for SQSTM1 variants.
Participants received ZA or placebo treatment and were followed up for 7 years.
Results:
ZA group showed significant improvement in bone lesions compared to the placebo group.
ZA treatment led to a reduction in bone resorption markers.
Conclusion:
Genetic screening and ZA treatment can be beneficial for individuals with a family history of PDB.
Further research is needed to determine the best approach for treatment.
Genetic Screening and Targeted Treatment Halt Paget Disease
Stats
An estimated 40%-50% of people with a familial history of PDB have pathogenic SQSTM1 variants.
29 lesions were found in the placebo group, compared to 15 in the ZA group.
Odds ratio for poor outcomes was 0.08 in the ZA group compared to the placebo group.
Quotes
"If it's positive, you should be able to have a bone scan and take it from there." - Stuart Ralston
"The bone scan reversal of abnormalities was amazing." - Stuart Ralston
"Now, it seems like [the test] is fairly easily available, so probably it's something we can begin to incorporate into our armamentarium." - Linda Russell
Key Insights Distilled From
by Lucy Hicks at www.medscape.com 01-15-2024
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/genetic-screening-targeted-treatment-halts-progression-paget-2024a10000wi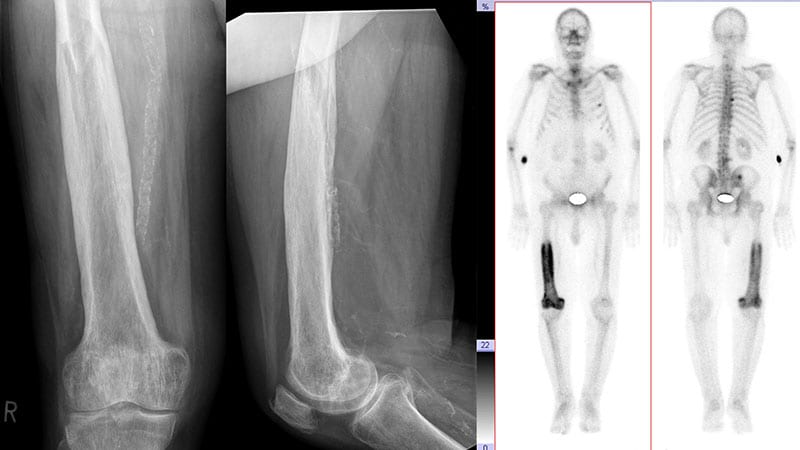
Deeper Inquiries
How can genetic screening and targeted treatment impact other bone-related disorders?
Genetic screening and targeted treatment can have a significant impact on other bone-related disorders by allowing for early identification of individuals at high risk for developing these conditions. By identifying specific genetic markers associated with certain bone disorders, healthcare providers can offer personalized preventive treatments to individuals before symptoms manifest. This proactive approach can potentially halt disease progression, prevent irreversible skeletal damage, and improve health outcomes. Furthermore, genetic screening can help in understanding the underlying mechanisms of various bone disorders, leading to the development of more targeted and effective treatment strategies for these conditions.
What are the potential drawbacks or limitations of using zoledronic acid for preventive treatment?
While zoledronic acid (ZA) has shown promising results in preventing the development or progression of Paget disease of the bone (PDB) in individuals at high genetic risk, there are potential drawbacks and limitations to consider. One limitation is the need for intravenous administration, which may not be suitable for all individuals and can pose logistical challenges in terms of accessibility and administration. Additionally, long-term use of ZA may be associated with adverse effects such as osteonecrosis of the jaw, atypical femoral fractures, and renal impairment. Monitoring for these potential side effects and managing them appropriately is crucial when considering ZA as a preventive treatment. Furthermore, the cost of ZA treatment and the sustainability of long-term preventive strategies using this medication may also be limiting factors that need to be taken into account.
How can the views of individuals with a family history of PDB influence future research and treatment approaches?
The views of individuals with a family history of Paget disease of the bone (PDB) can play a crucial role in shaping future research and treatment approaches for the condition. By gathering insights from these individuals, researchers and healthcare providers can better understand the impact of PDB on affected families, the challenges they face in managing the disease, and their preferences regarding preventive strategies and treatment options. Incorporating the perspectives of individuals with a familial history of PDB can help in designing more patient-centered research studies, developing tailored interventions that address the specific needs of this population, and improving the overall quality of care provided to individuals at risk for PDB. Additionally, involving patients in decision-making processes regarding their healthcare can lead to more effective and sustainable treatment approaches that are aligned with their values, preferences, and experiences.
0
More on Healthcare
