Measuring Muscle Mass in Heart Failure Patients
Core Concepts
Mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) and arm muscle circumference (AMC) are more prognostic in heart failure patients than guideline-recommended skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) or calf circumference (CC).
Abstract
In a study of over 800 heart failure patients, MUAC and AMC were found to be more predictive of prognosis than SMI or CC. The findings challenge current sarcopenia guidelines, suggesting that MUAC and AMC may be more useful in risk stratification and treatment strategies for heart failure patients. However, caution is advised, and further research is needed to validate these results.
- MUAC and AMC were associated with better prognoses than SMI and CC.
- Skeletal muscle mass assessment in heart failure patients is challenging due to fluid retention.
- MUAC and AMC may offer valuable insights for risk stratification and treatment strategies.
- Methodological weaknesses and the need for prospective studies were highlighted by experts.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.medscape.com
How Should Muscle Mass Be Measured in Heart Failure?
Stats
High MUAC (hazard ratio [HR], for combined events, 0.590) and high AMC (HR for combined events, 0.529) were associated with significantly better prognoses than low MUAC and low AMC.
The study included 869 patients with a median age of 73 years and a follow-up period of 1.24 years.
High MUAC and high AMC groups were associated with better prognoses after adjusting for various factors.
Quotes
"These findings challenge the current recommendations found in sarcopenia guidelines."
"When caring for patients with heart failure, it seems that the often overlooked and simple measure of arm circumference might carry significant prognostic value."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Marilynn Lar... at www.medscape.com 08-23-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/995763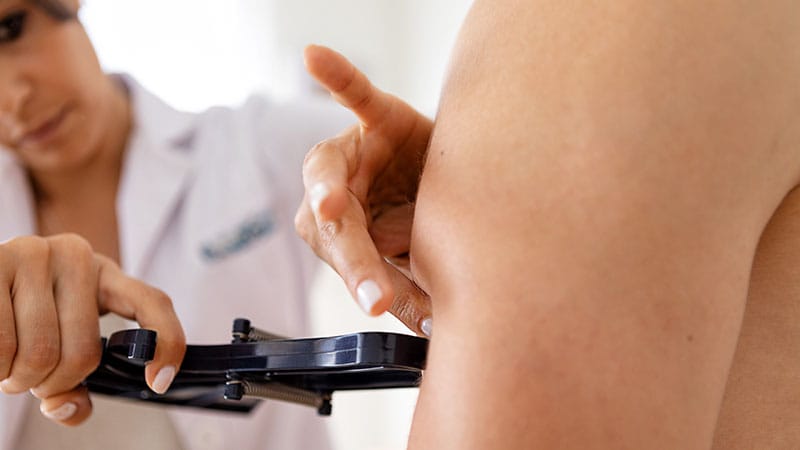
Deeper Inquiries
How can MUAC and AMC measurements be integrated into current clinical practices for heart failure patients?
The integration of mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) and arm muscle circumference (AMC) measurements into current clinical practices for heart failure patients can provide valuable prognostic information and aid in risk stratification for sarcopenia. These measurements, which have shown significant associations with better outcomes in heart failure patients compared to traditional methods like skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) or calf circumference (CC), can be incorporated into routine assessments during patient evaluations. Healthcare providers can easily measure MUAC and AMC using a plastic tape measure and a skinfold caliper, making it a simple and cost-effective addition to existing protocols. By including these anthropometric measurements in regular assessments, clinicians can better identify patients at higher risk for adverse outcomes and tailor treatment strategies accordingly.
What are the potential implications of these findings on existing guidelines for sarcopenia assessment?
The findings regarding the prognostic value of MUAC and AMC measurements in heart failure patients challenge the current recommendations in existing guidelines for sarcopenia assessment. Traditional guidelines, such as those from the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People and the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia, emphasize the use of SMI and CC measured through bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) for screening skeletal muscle mass. However, the study suggests that MUAC and AMC may be more strongly associated with prognosis in heart failure patients. These results could potentially lead to a reevaluation of current guidelines and a consideration for incorporating MUAC and AMC measurements as part of routine assessments for sarcopenia in this patient population. Further research and validation of these findings in diverse patient cohorts are necessary before any changes to existing guidelines can be recommended.
How might the inclusion of anthropometric measurements impact the overall management of heart failure patients?
The inclusion of anthropometric measurements, specifically MUAC and AMC, in the assessment of heart failure patients can have significant implications for their overall management. By utilizing these simple and easily accessible measurements, healthcare providers can better identify patients at risk for adverse outcomes related to sarcopenia. This information can help in risk stratification, treatment planning, and monitoring of patients with heart failure. Clinicians can use MUAC and AMC measurements to tailor interventions aimed at improving muscle mass and strength, which are crucial for the overall well-being and prognosis of heart failure patients. Additionally, the incorporation of these anthropometric measurements into routine clinical practice may lead to a more holistic approach to managing heart failure, considering not only cardiac function but also skeletal muscle health. This comprehensive assessment can potentially improve patient outcomes and quality of life in individuals with heart failure.
0
