Robotic Patients in Medical Training: Benefits and Limitations
Core Concepts
Robotic patient simulators offer valuable training opportunities but come with limitations that must be carefully considered.
Abstract
The content discusses the use of robotic patient simulators in medical training, focusing on HAL s5301, an advanced patient simulator. It highlights the benefits and limitations of using simulators in medical education, emphasizing the educational worth and the potential risks associated with their use. The article also explores the comparison between robotic simulators and virtual reality techniques, as well as the importance of proper training and feedback in maximizing the effectiveness of simulator-based learning.
Overview
- Introduction of HAL s5301, an advanced patient simulator used for medical training.
- Simulation in medical teaching history and the evolution of simulators.
- Benefits of simulators in honing medical skills and improving student competence.
- Comparison between robotic simulators and virtual reality techniques.
- Risks and limitations associated with simulator-based training.
- Importance of proper training and feedback for effective simulator use.
Benefits of Robotic Simulators
- HAL s5301's capabilities in simulating various medical scenarios.
- Use of simulators for practicing key medical techniques and procedures.
- Reproduction of physiological functions for realistic training experiences.
- Debrief sessions for error identification and skill improvement.
Evolution of Medical Simulation
- Historical background of simulation in medical education.
- Introduction of robotic simulators like Sim One and Harvey.
- Studies showing the benefits of simulators in enhancing diagnostic and surgical skills.
- Use of high-fidelity simulators in medical curricula.
Virtual Alternatives and Cost Considerations
- Comparison between robotic simulators and virtual reality techniques.
- Cost implications of using simulators in medical training.
- Studies on the effectiveness of simulators in improving patient outcomes.
- Plans for future studies to analyze skill acquisition through simulation.
Risks and Limitations
- Challenges in accurately imitating all symptoms and types of illnesses.
- Potential risks of misleading training outcomes.
- Imperfect anatomical accuracy of mannequin simulators.
- Importance of properly trained teachers for effective simulator use.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.medscape.com
Robotic Patients? They're Useful but Have Limitations
Stats
HAL s5301 costs around $100,000.
Service costs for HAL s5301 amount to $16,000.
Up to $250,000 can be expected to be paid for a realistic simulator.
Quotes
"This experience was essential to my learning, because it meant that by the time I got to my hospital placement, I already felt pretty confident in my ability to approach patients and how to correctly distinguish different clinical signs." - Miriam Rosso
"It's my belief that, if a student learns incorrectly, the cause will never be the simulator's lack of realism, but rather a failing on the part of the person who planned the activity or supported it as a tutor or facilitator." - Grazia Papotti
Key Insights Distilled From
by Massimo Sand... at www.medscape.com 08-22-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/robotic-patients-they-re-useful-have-limitations-2023a1000jev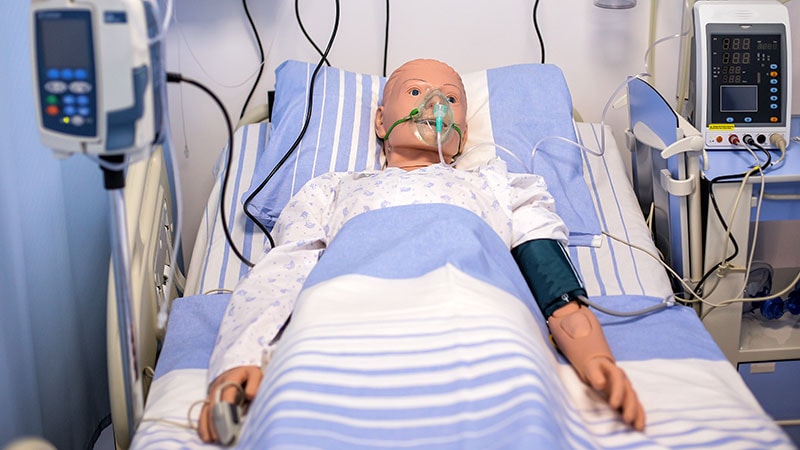
Deeper Inquiries
How can the use of simulator mannequins be optimized to ensure better patient outcomes?
To optimize the use of simulator mannequins for better patient outcomes, several key strategies can be implemented. Firstly, it is essential to ensure that the simulation scenarios are as realistic and diverse as possible, incorporating a wide range of symptoms and medical conditions to mimic real-life situations accurately. This can help students develop critical thinking skills and adaptability in diagnosing and treating patients.
Secondly, providing comprehensive feedback and debriefing sessions after each simulation is crucial. This feedback should not only focus on technical skills but also on communication, teamwork, and decision-making abilities. By receiving constructive feedback, students can identify areas for improvement and enhance their overall performance.
Moreover, incorporating virtual patient interactions and incorporating human feedback during simulations can further enhance the learning experience. This can help students develop empathy, communication skills, and bedside manner, which are essential for building strong doctor-patient relationships and improving patient outcomes.
Lastly, continuous training and assessment using simulator mannequins are vital to ensure that students retain and apply their skills effectively in clinical practice. By regularly engaging in simulation-based training, medical professionals can stay updated on the latest medical practices and technologies, ultimately leading to better patient care and outcomes.
How can the potential drawbacks of relying too heavily on simulator-based training in medical education be mitigated?
While simulator-based training offers numerous benefits, there are potential drawbacks that need to be addressed to ensure a well-rounded medical education. One significant drawback is the risk of over-reliance on simulators, which may lead to a lack of exposure to real patient interactions and clinical settings. To mitigate this risk, a balanced approach that combines simulator-based training with clinical rotations and hands-on experience is essential.
Another drawback is the cost associated with high-fidelity simulators, which may limit access for some educational institutions. To address this issue, collaborative efforts between institutions, industry partners, and government agencies can help secure funding and resources to make simulator training more accessible to a wider range of students.
Furthermore, ongoing research and evaluation of simulator-based training programs are crucial to ensure their effectiveness and relevance in medical education. By continuously assessing the impact of simulator training on student learning outcomes and patient care, educators can make informed decisions on how to optimize and improve these programs.
Overall, by acknowledging the potential drawbacks of simulator-based training and implementing strategies to mitigate these challenges, medical educators can create a comprehensive and effective training curriculum that prepares students for successful clinical practice.
How can the integration of virtual reality techniques enhance the effectiveness of medical simulation training?
The integration of virtual reality (VR) techniques in medical simulation training can significantly enhance the learning experience and effectiveness of training programs. VR technology offers a highly immersive and interactive environment that allows students to practice clinical skills in a realistic and controlled setting.
One key advantage of VR techniques is their cost-effectiveness compared to high-fidelity simulators. VR simulations can be easily accessed and deployed on standard devices, making them more accessible to a broader audience of students and institutions.
Moreover, VR simulations can provide a safe space for students to practice complex procedures and scenarios repeatedly, without the risk of harm to real patients. This repetitive practice can help students build muscle memory, improve decision-making skills, and enhance their overall proficiency in various medical procedures.
Additionally, VR simulations can offer a high level of customization and adaptability, allowing educators to create tailored training scenarios based on specific learning objectives and student needs. This personalized approach can cater to individual learning styles and preferences, ultimately leading to better engagement and knowledge retention among students.
Overall, the integration of VR techniques in medical simulation training can revolutionize the way medical education is delivered, offering a dynamic and interactive learning experience that prepares students for the complexities of clinical practice.
0
