Tripeptide-Based Glass with Optical, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Properties
The article discusses the surprising discovery that a glass can be made from an organic compound as simple as a tripeptide, which consists of a linear chain of just three amino-acid residues. This new glass material has optical properties similar to those of conventional glass, but also exhibits adhesive and self-healing capabilities.
Glass has long been a material that has shaped society through the ages. The main ingredients of conventional glass are modest - sand, limestone, and sodium carbonate. However, these raw materials can be crafted into fine luxury objects. The term 'glass' refers to a state of matter rather than a chemical composition, describing any substance that has been cooled to rigidity without becoming crystalline.
The researchers report that this new tripeptide-based glass material has properties that are distinct from conventional glass. In addition to the optical similarities, the material also demonstrates adhesive and self-healing capabilities, which are unique features. This discovery showcases the potential of using simple organic compounds to create advanced glass materials with novel functionalities beyond the limitations of traditional glass compositions.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
Self-healing glass from a simple peptide — just add water
Key Insights Distilled From
by Silvia March... at www.nature.com 06-12-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-01505-7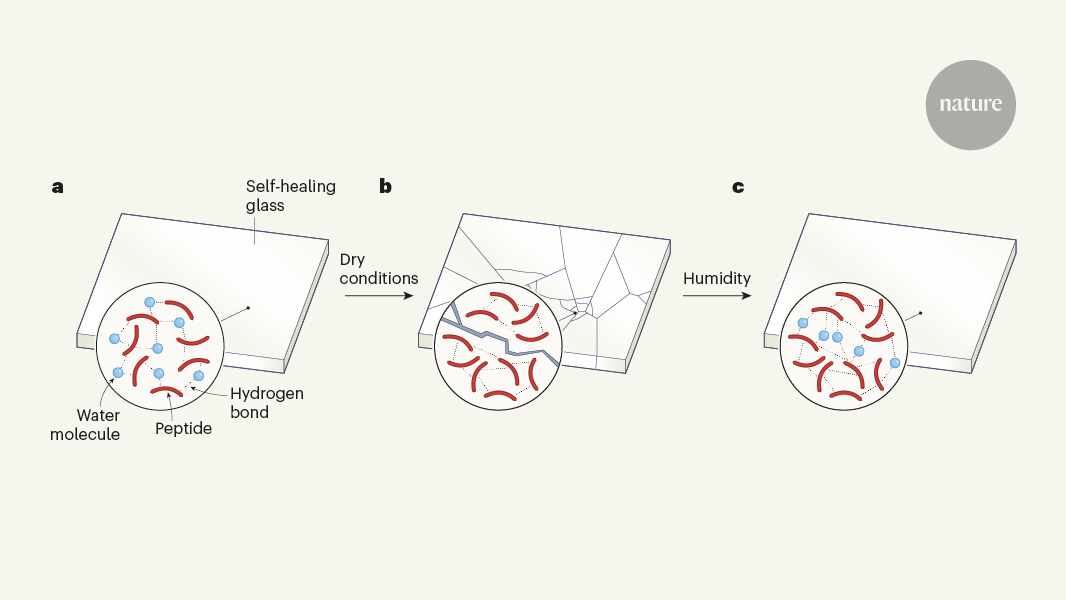
Deeper Inquiries
