Predicting Immune-related Adverse Events in Melanoma Patients Using Histopathology Reports
Core Concepts
Histopathology reports in melanoma patients can predict immune-related adverse events during checkpoint inhibitor treatment.
Abstract
TOPLINE:
Routine histopathology reports can predict immune-related adverse events in melanoma patients on checkpoint inhibitors.
METHODOLOGY:
Study evaluated melanoma histopathology to predict immune-related adverse events.
Retrospective review of 511 melanoma patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
Two-stage regression analysis on tumor histopathology and immune-related adverse events.
TAKEAWAY:
Pembrolizumab and nivolumab were the most used checkpoint inhibitors.
40% of patients changed inhibitors due to adverse events.
Most patients experienced all-grade toxicities.
Two histopathological features linked to all-grade adverse events.
IN PRACTICE:
Presence of lymphovascular invasion and NRAS mutation associated with increased odds of adverse events.
SOURCE:
Research by Catherina X. Pan, Vinod E. Nambudiri, and Nicole R. LeBoeuf from Brigham and Women's Hospital.
LIMITATIONS:
Retrospective analysis may lack generalizability due to institutional variations.
DISCLOSURES:
Authors have various consulting and honoraria relationships.
ICIs in Melanoma: Predicting Immune-related Adverse Events
Stats
Approximately 40% of patients stopped or changed checkpoint inhibitors due to immune-related adverse events.
Most patients (71.4%) experienced all-grade toxicities, and 28.2% experienced high-grade toxicities.
Patients with indeterminate lymphovascular invasion had significantly lower odds of developing all-grade immune-related adverse events than patients with lymphovascular invasion (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.36).
The presence of NRAS mutation increased the patients' odds of developing all-grade immune-related adverse events (aOR, 2.56).
Quotes
"Routine histopathology reports may allow physicians to predict which patients with melanoma are the most likely to develop immune-related adverse events while taking checkpoint inhibitors."
"The presence of lymphovascular invasion and NRAS mutation were associated with increased odds of all-grade immune-related adverse events."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Helen Leask at www.medscape.com 12-26-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/predicting-immune-related-adverse-events-checkpoint-2023a1000wml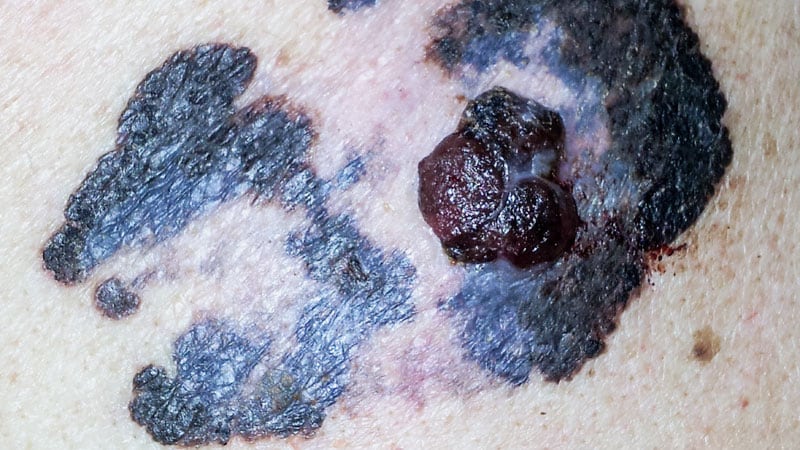
Deeper Inquiries
How can histopathology reports be effectively utilized in clinical practice to predict immune-related adverse events in melanoma patients
Histopathology reports can play a crucial role in predicting immune-related adverse events in melanoma patients by providing valuable insights into the tumor characteristics that may influence the likelihood of such events occurring. In the context of this study, the researchers identified specific histopathological features, such as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, regression, ulceration, mitotic rate, lymphovascular invasion, histological subtype, anatomic location, and BRAF/NRAS mutation, that were associated with immune-related adverse events. By analyzing these features, clinicians can potentially stratify patients based on their risk profile for developing such events while undergoing treatment with checkpoint inhibitors. This risk stratification can help in implementing proactive monitoring strategies, early intervention, and personalized treatment approaches to mitigate the impact of immune-related adverse events on patient outcomes.
What are the potential implications of the study findings on the current treatment strategies for melanoma patients
The study findings have significant implications for current treatment strategies for melanoma patients, particularly those receiving checkpoint inhibitors. By identifying histopathological features that are predictive of immune-related adverse events, clinicians can tailor their approach to patient management more effectively. For instance, patients with specific histopathological characteristics, such as lymphovascular invasion or NRAS mutation, may require closer monitoring or alternative treatment strategies to minimize the risk of developing immune-related adverse events. Additionally, these findings may contribute to the development of personalized medicine approaches in melanoma treatment, where treatment decisions are guided by the individual patient's tumor characteristics to optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing the occurrence of adverse events.
How can the variability in institutional interpretation of histopathology reports impact the overall reliability of the study results
The variability in institutional interpretation of histopathology reports can potentially impact the overall reliability of the study results by introducing inconsistencies in the assessment of histopathological features associated with immune-related adverse events. Since the analysis in this study was retrospective and involved data from multiple centers, differences in how histopathology reports are interpreted and documented across institutions could lead to variations in the identification and characterization of relevant tumor features. This variability may affect the accuracy and generalizability of the findings, highlighting the importance of standardizing histopathology reporting practices to ensure consistency in assessing the predictive value of tumor characteristics for immune-related adverse events in melanoma patients.
0
