Sirolimus Treatment for Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Study Results
Core Concepts
Sirolimus shows promise in treating cutaneous sarcoidosis.
Abstract
The study explores the effectiveness of sirolimus in treating cutaneous sarcoidosis, highlighting improvements in skin lesions. Key points include:
Sirolimus treatment led to improvements in skin lesions in 7 out of 10 patients.
Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibition is a potential therapeutic avenue for sarcoidosis.
Previous studies have shown high mTOR activity in sarcoidosis granulomas.
The study involved a small clinical trial with 16 participants.
Sirolimus treatment resulted in clinical improvement in skin lesions, with some patients experiencing complete resolution.
No serious adverse events were reported, but mild skin reactions were noted in some patients.
The study suggests the need for larger clinical trials to further explore mTOR inhibition in sarcoidosis.
Molecular analysis combined with clinical response supports the relevance of the mTOR pathway in sarcoid granuloma formation.
Targeting mTOR Shows Promise in Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
Stats
7 of 10 patients treated with sirolimus had improvements in skin lesions after 4 months.
70% of patients in the systemic group had clinical improvement in skin lesions.
The median change in Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Activity and Morphology Index was -7.0 points.
42% of patients treated with systemic sirolimus reported mild skin reactions.
Adverse events included hypertriglyceridemia (17%), hyperglycemia (17%), and proteinuria (8%).
Quotes
"Although all reports observed improvement of the disease following the treatment, no clinical trial investigating the efficacy and safety of sirolimus in patients with sarcoidosis had been published" - Georg Stary, MD
Key Insights Distilled From
by Lucy Hicks at www.medscape.com 01-31-2024
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/targeting-mtor-shows-promise-cutaneous-sarcoidosis-2024a100024b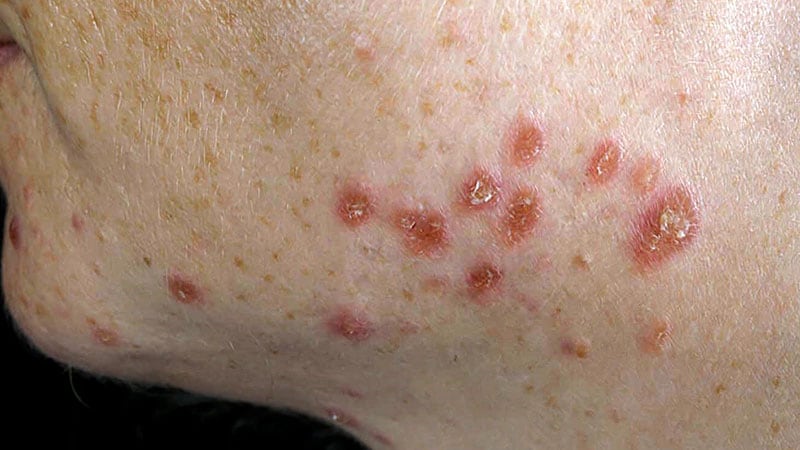
Deeper Inquiries
How can larger clinical trials address the challenges of studying rare diseases like sarcoidosis
Larger clinical trials can address the challenges of studying rare diseases like sarcoidosis by allowing for a more diverse and representative sample of patients. With a larger pool of participants, researchers can better understand the variability in disease presentation, demographics, and treatment responses. This can lead to more robust findings that are applicable to a broader population. Additionally, larger trials can provide more statistical power to detect significant treatment effects, especially in rare diseases where individual responses may vary widely. By including a more diverse group of patients, researchers can also explore potential subgroups that may respond differently to treatment, leading to personalized approaches in managing sarcoidosis.
What are the potential implications of mTOR inhibition in treating sarcoidosis in organs beyond the skin
The potential implications of mTOR inhibition in treating sarcoidosis in organs beyond the skin are significant. Since mTOR activity has been detected in sarcoidosis granulomas in various organs like the lung and heart, targeting mTOR could have systemic effects on the disease. If mTOR upregulation is indeed a key factor in sarcoid granuloma formation, as suggested by this study, then inhibiting mTOR could potentially benefit patients with sarcoidosis affecting multiple organs. This could open up new avenues for treating systemic sarcoidosis and may lead to more comprehensive and effective therapeutic strategies that target the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
How can the findings of this study impact the development of treatment strategies for sarcoidosis
The findings of this study can have a substantial impact on the development of treatment strategies for sarcoidosis. By demonstrating the efficacy of sirolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, in improving skin lesions in patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis, the study highlights the potential of targeting the mTOR pathway as a therapeutic approach. These results suggest that mTOR inhibition could be a promising treatment option for sarcoidosis, not only in the skin but potentially in other affected organs as well. This could lead to the development of novel therapies that specifically target mTOR activity in sarcoidosis, offering new hope for patients with this challenging disease. Additionally, the study's focus on sustained treatment effects and molecular analysis provides valuable insights that can guide future research and clinical trials in exploring mTOR inhibition as a viable treatment strategy for sarcoidosis.
0
More on Medical Research
