Esophageal Fistula Complications in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
Core Concepts
Esophageal fistula complications in atrial fibrillation ablation have high mortality rates and require prompt diagnosis and management.
Abstract
The content discusses the rare but serious complication of esophageal fistula (EF) following catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF). The POTTER AF study highlighted a 65.8% mortality rate for EF cases, emphasizing the importance of timely diagnosis and appropriate management strategies. Delays in diagnosis, common symptoms, diagnostic modalities, treatment methods, and outcomes are detailed. Surgery was associated with the lowest mortality rate, reducing the risk of death by about 68%. The study also highlighted the limitations and challenges in managing EF complications.
- Rare but serious complication of catheter ablation for AF
- POTTER AF study: 65.8% mortality rate for EF cases
- Delays in diagnosis, common symptoms, diagnostic modalities
- Treatment methods and outcomes
- Surgery associated with the lowest mortality rate
- Limitations and challenges in managing EF complications
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.medscape.com
CT and Surgery Best Diagnose and Manage Esophageal Fistula
Stats
The incidence of esophageal fistula was 0.025%, approximately 25 per 100,000 patients.
Death occurred in 65.8% of EF cases.
Surgery was associated with a mortality odds ratio of 0.321.
Conservative management had a mortality odds ratio of 7.463.
Quotes
"I promise you that you will have a very clear plan how to diagnose and treat patients with esophageal fistula once you have seen this presentation." - Prof Roland Tilz
Key Insights Distilled From
by Daniel M. Ke... at www.medscape.com 04-18-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/990933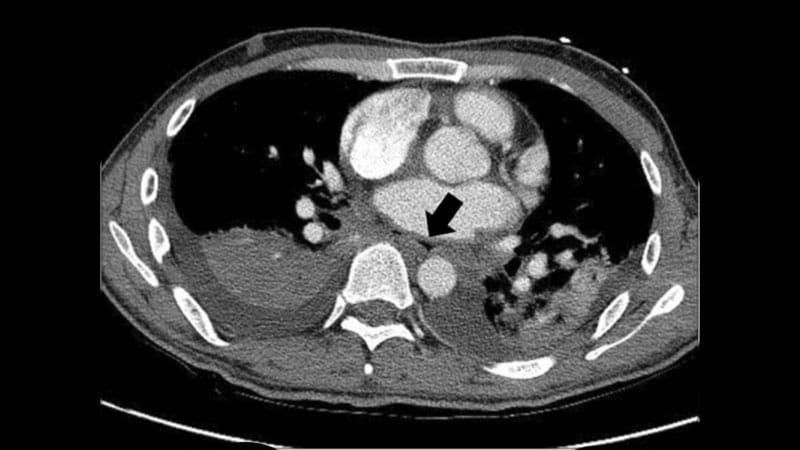
Deeper Inquiries
What advancements in catheter ablation techniques could potentially reduce the risk of esophageal fistula complications?
Esophageal fistula (EF) is a serious complication of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF), with high mortality rates. Advancements in catheter ablation techniques could potentially reduce the risk of EF complications. One such advancement is the utilization of cryo energy instead of radiofrequency (RF) energy during ablation procedures. Studies have shown that cryo energy carries a significantly lower risk of EF compared to RF ablation. By adopting cryo energy as the primary energy source for ablation, the incidence of EF could potentially be reduced. Additionally, improvements in catheter design and technology to enhance precision and accuracy during ablation procedures may also contribute to lowering the risk of EF complications.
Is there a role for preventive measures in reducing the incidence of esophageal fistula following AF ablation procedures?
Preventive measures can play a crucial role in reducing the incidence of esophageal fistula following AF ablation procedures. One key preventive measure is ensuring proper patient selection and thorough pre-procedural evaluation to identify individuals at higher risk for developing EF. This includes assessing anatomical variations that may predispose patients to esophageal injury during ablation. Implementing stringent protocols for monitoring and managing esophageal temperature during the procedure can also help prevent thermal injury to the esophagus, reducing the risk of EF. Moreover, optimizing ablation techniques to minimize energy delivery to the esophageal wall and employing imaging modalities such as intracardiac echocardiography to guide catheter placement can further enhance safety and reduce the likelihood of EF occurrence.
How can the medical community improve reporting and data collection to better understand the true incidence and risk factors associated with esophageal fistula complications?
To better understand the true incidence and risk factors associated with esophageal fistula complications, the medical community can take several steps to improve reporting and data collection. One approach is to establish standardized reporting mechanisms for EF cases, ensuring that all instances are documented and reported consistently across healthcare institutions. This can help create a comprehensive database of EF cases, enabling researchers to analyze trends and identify potential risk factors. Collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, regulatory bodies, and professional societies can facilitate the sharing of data and insights, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of EF complications. Additionally, conducting prospective studies with detailed data collection on procedural variables, patient characteristics, and outcomes can provide valuable insights into the incidence and predictors of EF, guiding the development of preventive strategies and treatment protocols. By enhancing reporting practices and data collection efforts, the medical community can advance knowledge and improve outcomes for patients at risk of esophageal fistula following AF ablation procedures.
0
