Genetically Modified Pig Kidneys in Human Transplantation
Core Concepts
Genetically modified pig kidneys demonstrate life-sustaining function in human transplantation.
Abstract
The content discusses a groundbreaking experiment where genetically modified pig kidneys were transplanted into a brain-dead patient, showcasing their ability to filter blood and produce urine. The study, published in JAMA Surgery, highlights the potential of xenotransplantation as a solution to the organ shortage crisis in end-stage kidney disease patients.
Key Highlights:
Genetically modified pig kidneys transplanted into a brain-dead patient functioned for 7 days.
The recipient received standard immunosuppression and showed positive kidney function indicators.
Previous experiments by the same team showed delayed kidney function, but this time, urine production was observed within minutes.
The study suggests that xenotransplantation with pig kidneys could be a viable alternative for human organ transplants.
Long-term outcomes and generalizability of the findings require further research.
Pig Kidneys Show 'Life-Sustaining' Function in Human
Stats
During the first 24 hours after transplantation, the pig kidneys made more than 37 liters of urine.
At the end of the study, the serum creatinine level was 0.9 mg/dL, and creatinine clearance was 200 mL/min.
Quotes
"It was really a remarkable thing to see." - Jayme Locke, MD
"This new work firmly establishes that the xenografts not only make urine but provide life-sustaining kidney function by clearing serum creatinine." - Locke
Key Insights Distilled From
by Lori Youmsha... at www.medscape.com 08-16-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/995532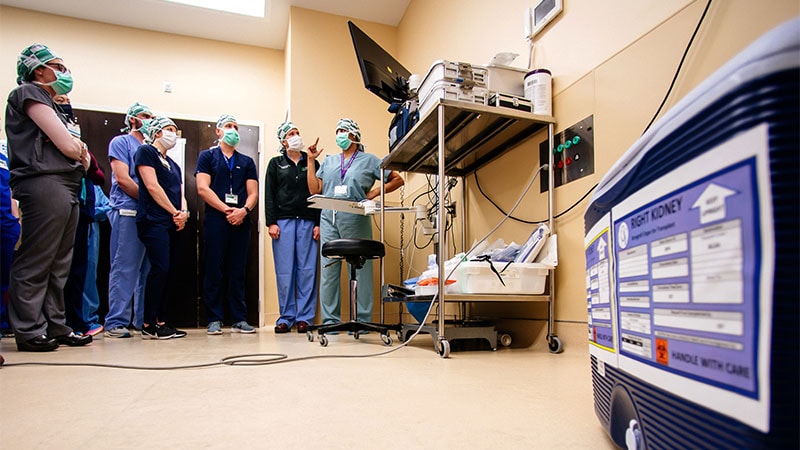
Deeper Inquiries
How might xenotransplantation impact the future of organ transplantation?
Xenotransplantation has the potential to revolutionize the field of organ transplantation by addressing the critical shortage of human organs available for patients in need. By utilizing genetically modified animal organs, such as pig kidneys in this case, xenotransplantation offers a promising solution to the organ shortage crisis. If successful in the long term, xenotransplantation could significantly increase the availability of organs for transplantation, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for patients with end-stage organ failure.
What ethical considerations arise from using genetically modified animal organs in humans?
The use of genetically modified animal organs in humans raises several ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. One of the primary concerns is the welfare of the animals involved in the research and organ harvesting process. Ethical guidelines must ensure that animals are treated humanely and that their genetic modification is conducted responsibly. Additionally, there are ethical implications regarding the potential risks and uncertainties associated with xenotransplantation, such as the long-term effects of animal-to-human organ transplantation and the possibility of organ rejection. Ensuring informed consent, transparency, and ongoing monitoring of both animal and human subjects are essential ethical considerations in xenotransplantation research.
How can advancements in xenotransplantation research benefit other fields of medicine?
Advancements in xenotransplantation research have the potential to benefit a wide range of fields within medicine. The development of genetically modified animal organs for transplantation could have implications beyond organ transplantation, such as in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. By understanding the mechanisms of immune response and organ compatibility in xenotransplantation, researchers can apply this knowledge to improve treatments for autoimmune diseases, cancer immunotherapy, and other conditions where immune responses play a critical role. Furthermore, the technologies and techniques developed in xenotransplantation research can be adapted and applied to other areas of medicine, leading to innovative therapies and medical advancements across various disciplines.
0
