Alarming Lack of Diabetes Complication Screening in Latin America and the Caribbean
Core Concepts
Diabetes patients in Latin America and the Caribbean are not receiving recommended eye and foot examinations to prevent serious complications like retinopathy and neuropathy.
Abstract
The study analyzed data from national surveys in 9 Latin American and Caribbean countries and found concerning gaps in the implementation of diabetes complication prevention measures:
Only 3 territories (Chile, Brazil, British Virgin Islands) had more than 50% of diabetes patients receive an eye exam in the previous 2 years.
The rate of foot assessments was below 41% in all countries in the previous year.
Older patients and those on insulin/oral hypoglycemic medications were more likely to undergo these preventive screenings.
Factors contributing to the poor results include patient-level barriers like lack of knowledge and empowerment, as well as healthcare system issues like limited access, consultation times, and specialized resources.
The researchers emphasize the need for public policies and health system improvements to prioritize primary care, education, and prevention of diabetes complications to improve patient outcomes and reduce the high costs of treating advanced complications.
Innovative approaches using technology like chatbots and telemedicine could help expand access to preventive services, especially in resource-limited settings.
Prevention of Diabetes Complications Lags in Latin America
Stats
Only 3 out of 9 countries had more than 50% of diabetes patients receive an eye exam in the previous 2 years.
The rate of foot assessments was below 41% in all 9 countries in the previous year.
Older patients (age 55-64) and those on insulin/oral hypoglycemic medications were more likely to undergo preventive screenings.
Quotes
"These numbers are concerning. Patients with diabetes are at risk of developing retinopathy and neuropathy, which can lead to amputations. Without prevention, this risk increases."
"You can't improve what you don't measure, and having concrete data is the first step in designing and implementing strategies to optimize the quality of care and reduce the dreaded complications of diabetes."
"At this point, I believe that the development of public policies that guide the available resources to primary care, education, and prevention of complications is fundamental. This will improve the quality of life of people with diabetes and reduce the high costs of treating advanced complications."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Fernando at www.medscape.com 05-10-2024
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/prevention-diabetes-complications-lags-latin-america-2024a10008zl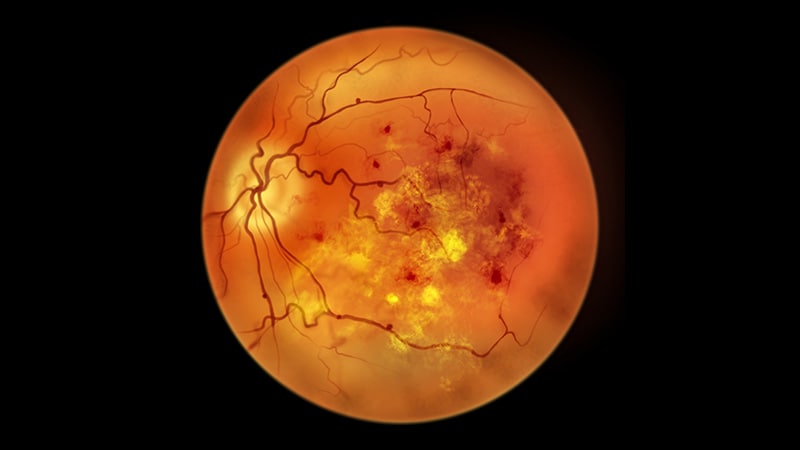
Deeper Inquiries
What specific barriers within the healthcare systems of these Latin American and Caribbean countries contribute to the low rates of diabetes complication screening?
The low rates of diabetes complication screening in Latin American and Caribbean countries can be attributed to various barriers within the healthcare systems. These barriers include limited access to care, inadequate consultation times, and a scarcity of specialized resources for preventive consultations. Additionally, factors such as lack of knowledge among patients, minimization of diabetes complications, and a lack of empowerment to demand regular evaluations also contribute to the low screening rates. Healthcare systems in these regions often face challenges in allocating resources effectively towards primary care, education, and prevention of complications, further hindering the screening process for diabetes-related complications.
How can patient education and empowerment strategies be tailored to overcome the identified patient-level barriers to seeking preventive care?
To overcome the patient-level barriers to seeking preventive care for diabetes-related complications, tailored patient education and empowerment strategies are essential. These strategies should focus on increasing awareness about the importance of regular screenings for complications like retinopathy and neuropathy. Patients need to be educated on the potential risks associated with diabetes and the benefits of early detection and prevention. Empowering patients to take charge of their health by encouraging them to request regular evaluations, providing them with information on self-care practices, and involving them in decision-making processes regarding their healthcare can help overcome barriers to seeking preventive care.
What innovative digital health technologies have the potential to expand access to diabetes eye and foot examinations in resource-limited settings, and how can their implementation be studied and scaled?
In resource-limited settings, innovative digital health technologies can play a crucial role in expanding access to diabetes eye and foot examinations. Technologies such as telemedicine, mobile health applications, and remote monitoring devices can facilitate remote consultations, provide educational materials, and enable patients to track their health status. Implementing chatbots for educational purposes, utilizing text messages for reminders and educational content, and offering video consultations for remote screenings can enhance access to eye and foot examinations for patients with diabetes. These technologies can be studied through implementation research that evaluates their effectiveness, acceptance by patients, and scalability in different healthcare settings. By understanding the impact of these digital health tools on improving screening rates and patient outcomes, healthcare providers can scale up their implementation to benefit a larger population of individuals with diabetes.
0
