EULAR Imaging Recommendations for Gout and CPPD
Core Concepts
Imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring crystal-induced arthropathies, with specific modalities recommended for gout, BCPD, and CPPD.
Abstract
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) released new guidance on imaging for crystal-induced arthropathies (CiA), emphasizing the importance of imaging in diagnosing and monitoring these diseases. The recommendations cover the use of ultrasound (US) and dual-energy CT (DECT) for gout, conventional radiography or US for BCPD, and CT for CPPD. Imaging can aid in patient counseling, diagnosis, and predicting disease flares. The document also highlights the need for further research to enhance imaging's role in CiA diagnosis and treatment.
- EULAR releases new guidance on imaging for crystal-induced arthropathies (CiA).
- Specific imaging modalities recommended for gout, BCPD, and CPPD.
- Importance of imaging in patient counseling, diagnosis, and predicting disease flares.
- Emphasis on the need for further research to enhance imaging's role in CiA diagnosis and treatment.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.medscape.com
EULAR Issues Imaging Recommendations for Gout, CPPD
Stats
"These are the first-ever EULAR recommendations on imaging in this group of diseases." - Dr. Peter Mandl
"Both ultrasound (US) and dual-energy CT (DECT) are the recommended imaging modalities in gout."
"Imaging is necessary in the diagnosis of BCPD, and clinicians should use either conventional radiography or US."
"The document does not recommend serial imaging for either BCPD or CPPD unless there has been an 'unsuspected change in clinical characteristics.'"
Quotes
"I think it's a very powerful way to counsel patients." - Dr. Sara Tedeschi
"It would be great to have an imaging modality someday that would help us differentiate between various types of calcium crystal." - Dr. Peter Mandl
Key Insights Distilled From
by Lucy Hicks at www.medscape.com 06-16-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/993336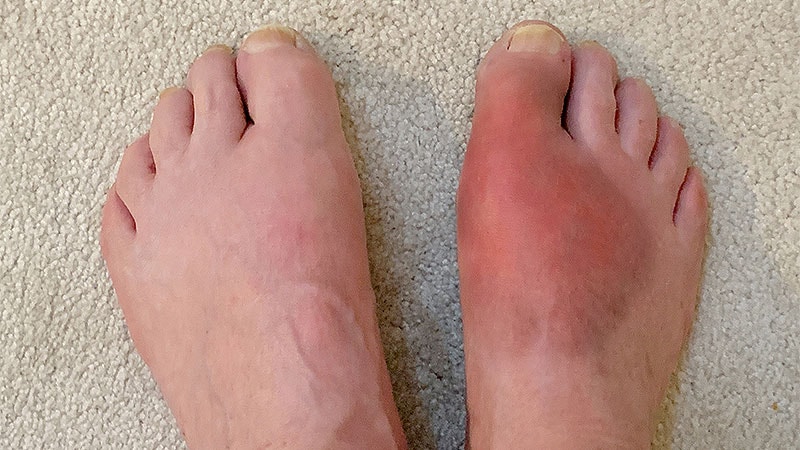
Deeper Inquiries
How can imaging advancements further improve the diagnosis and treatment of crystal-induced arthropathies?
Imaging advancements can significantly enhance the diagnosis and treatment of crystal-induced arthropathies by providing more accurate and detailed visualization of the affected areas. Techniques like ultrasound (US) and dual-energy CT (DECT) can offer high sensitivity and specificity for crystal deposition, aiding in early detection and monitoring of diseases like gout, basic calcium phosphate deposition disease (BCPD), and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD). By utilizing imaging modalities, clinicians can make more informed decisions regarding treatment strategies, predict disease flares based on crystal volume, and improve patient counseling by showing visual evidence of the condition. Additionally, ongoing research into new imaging modalities may eventually lead to tools that can differentiate between various types of calcium crystals, further refining diagnosis and treatment approaches.
What potential drawbacks or limitations might arise from relying heavily on imaging for diagnosis in rheumatology?
While imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosing crystal-induced arthropathies, there are potential drawbacks and limitations to consider when relying heavily on imaging for diagnosis in rheumatology. One limitation is the cost associated with imaging procedures, which may pose financial burdens on patients and healthcare systems. Additionally, over-reliance on imaging without clinical correlation can lead to unnecessary tests, procedures, and potential overdiagnosis or overtreatment. Interpretation of imaging findings requires expertise, and misinterpretation can result in incorrect diagnoses or treatment decisions. Furthermore, imaging may not always capture the full spectrum of disease activity or provide a comprehensive understanding of the patient's symptoms and overall clinical presentation. Therefore, a balanced approach that integrates imaging with clinical assessment is essential to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal patient care.
How can the integration of imaging technology in medical training programs enhance patient care and outcomes?
The integration of imaging technology in medical training programs can significantly enhance patient care and outcomes by equipping healthcare professionals with the skills and knowledge to effectively utilize imaging modalities in clinical practice. Training in ultrasound (US) and other imaging techniques during rheumatology fellowship programs can improve diagnostic accuracy, facilitate early detection of crystal-induced arthropathies, and enhance treatment monitoring. By incorporating imaging education into medical training, future healthcare providers can develop proficiency in interpreting imaging findings, correlating them with clinical symptoms, and making evidence-based treatment decisions. This integration can lead to more personalized and targeted patient care, improved communication with patients through visual aids, and ultimately better outcomes in the management of crystal-induced arthropathies.
0
