approfondimento - Cancer Research - # Concurrent Inhibition of Oncogenic and Wild-Type RAS-GTP for Cancer Therapy
Broad-Spectrum RAS Inhibitor Demonstrates Potent Activity Against Various RAS-Driven Cancers
Concetti Chiave
A reversible, tri-complex RAS inhibitor, RMC-7977, demonstrates potent activity against RAS-addicted tumors carrying various RAS genotypes, particularly KRAS codon 12 mutations, and can inhibit the growth of KRAS(G12C) cancer models resistant to existing KRAS(G12C) inhibitors.
Sintesi
The content discusses the development and preclinical evaluation of a novel RAS inhibitor, RMC-7977, which has broad-spectrum activity against both mutant and wild-type RAS isoforms. Key highlights:
RAS oncogenes, particularly KRAS, are among the most frequently mutated genes in cancer, but existing KRAS(G12C) inhibitors only target a subset of KRAS-mutated cancers.
RMC-7977 is a reversible, tri-complex RAS inhibitor that can target the active state of various RAS isoforms, including KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS.
Preclinically, RMC-7977 demonstrated potent activity against RAS-addicted tumors carrying diverse RAS genotypes, especially those with KRAS codon 12 mutations (KRAS(G12X)).
Treatment with RMC-7977 led to tumor regression and was well-tolerated in various RAS-addicted preclinical cancer models.
RMC-7977 was also able to inhibit the growth of KRAS(G12C) cancer models that are resistant to existing KRAS(G12C) inhibitors due to restoration of RAS pathway signaling.
A related RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitor, RMC-6236, is currently under clinical evaluation in patients with KRAS-mutant solid tumors.
Concurrent inhibition of oncogenic and wild-type RAS-GTP for cancer therapy - Nature
Statistiche
RAS oncogenes are among the most frequently mutated genes in cancer.
KRAS(G12C) mutations account for only around 15% of KRAS-mutated cancers.
RMC-7977 demonstrated potent activity against RAS-addicted tumors carrying various RAS genotypes, particularly KRAS codon 12 mutations.
Citazioni
"RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitors can target multiple oncogenic and wild-type RAS isoforms and have the potential to treat a wide range of RAS-addicted cancers with high unmet clinical need."
Approfondimenti chiave tratti da
by Matthew Hold... alle www.nature.com 04-08-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07205-6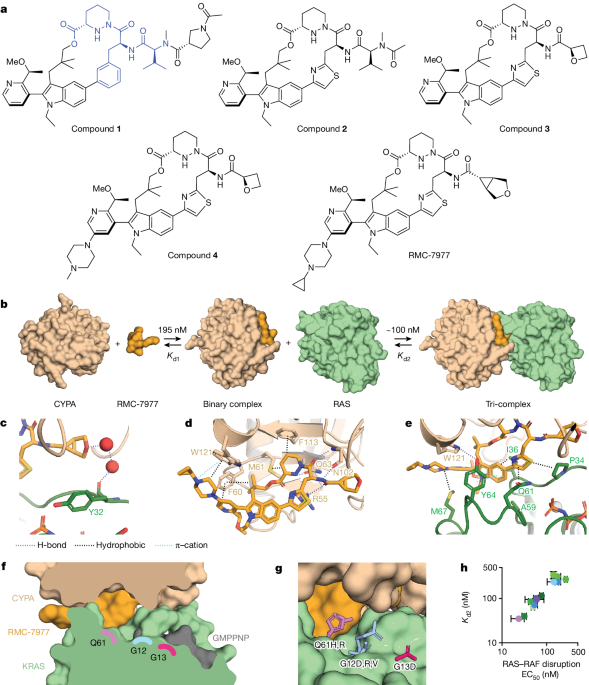
Domande più approfondite
What are the potential mechanisms by which RMC-7977 can overcome resistance to existing KRAS(G12C) inhibitors?
RMC-7977 can overcome resistance to existing KRAS(G12C) inhibitors through its unique mechanism of action as a reversible, tri-complex RAS inhibitor. Unlike traditional inhibitors that target specific mutations, RMC-7977 is a RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitor that can effectively inhibit both mutant and wild-type KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS variants. This broad-spectrum activity allows RMC-7977 to target multiple oncogenic and wild-type RAS isoforms, making it effective against a wide range of RAS-addicted cancers. In the context of KRAS(G12C) inhibitor resistance, RMC-7977 can inhibit the growth of cancer models that have developed resistance by restoring RAS pathway signaling. By targeting multiple RAS isoforms simultaneously, RMC-7977 offers a comprehensive approach to overcoming resistance mechanisms that may arise with single-target inhibitors.
How do the preclinical findings with RMC-7977 compare to other broad-spectrum RAS inhibitors in development?
The preclinical findings with RMC-7977 demonstrate its potent activity against RAS-addicted tumors carrying various RAS genotypes, particularly those with KRAS codon 12 mutations (KRASG12X). The efficacy of RMC-7977 in inducing tumor regression and its tolerability in diverse RAS-addicted preclinical cancer models highlight its potential as a promising therapeutic option for patients with RAS-mutated cancers. In comparison to other broad-spectrum RAS inhibitors in development, RMC-7977 stands out due to its tri-complex RAS inhibition and broad-spectrum activity against mutant and wild-type KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS variants. This multi-selective approach allows RMC-7977 to target a wider range of RAS-addicted cancers, including those with common KRAS mutations beyond KRAS(G12C). The preclinical data suggest that RMC-7977 may offer a more comprehensive and effective treatment strategy compared to other broad-spectrum RAS inhibitors currently under development.
What are the potential challenges and considerations in the clinical development of RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitors for cancer therapy?
The clinical development of RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitors, such as RMC-7977, presents several challenges and considerations. One key challenge is the need to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of these inhibitors in clinical trials, particularly in patients with diverse RAS-mutated cancers. Given the complexity of RAS signaling and the heterogeneity of RAS mutations, ensuring that RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitors effectively target the intended RAS isoforms without causing off-target effects is crucial. Additionally, identifying biomarkers that can predict response to RAS inhibitors and monitoring for the development of resistance mechanisms during treatment are important considerations in clinical development. Furthermore, optimizing dosing regimens and combination strategies to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitors while minimizing potential toxicities will be essential for successful clinical translation. Addressing these challenges and considerations will be critical for advancing RAS(ON) multi-selective inhibitors through clinical development and ultimately improving outcomes for patients with RAS-addicted cancers.
0
