Developing Antibody-Drug Conjugates for T Cell Cancers
핵심 개념
Developing antibody-drug conjugates for effective treatment of T cell cancers.
초록
The content discusses the development of antibody-drug conjugates for treating T cell cancers, focusing on targeting the T cell receptor β-chain constant region 1 (TRBC1). It highlights the challenges faced in previous clinical trials with anti-TRBC1 CAR T cells and introduces a new approach using an antibody-drug conjugate to overcome these challenges.
- Antibody and CAR T cell therapies have improved survival in various malignancies.
- T cell cancers lack targeted therapies, necessitating the development of new treatment approaches.
- Targeting TRBC1 shows promise in killing cancerous T cells while preserving healthy T cells.
- Clinical trials with anti-TRBC1 CAR T cells faced challenges due to low response rates and loss of efficacy.
- Development of an antibody-drug conjugate targeting TRBC1 shows potential in treating T cell cancers effectively.
요약 맞춤 설정
AI로 다시 쓰기
인용 생성
소스 번역
다른 언어로
마인드맵 생성
소스 콘텐츠 기반
소스 방문
www.nature.com
TRBC1-targeting antibody–drug conjugates for the treatment of T cell cancers - Nature
통계
Adults with T cell cancers have short survival.
Preclinical studies showed targeting TRBC1 can kill cancerous T cells while preserving healthy T cells.
First-in-human clinical trial of anti-TRBC1 CAR T cells reported a low response rate and loss of efficacy.
인용구
"The anti-TRBC1 antibody-drug conjugate may provide an optimal format for TRBC1 targeting and produce superior responses in patients with T cell cancers."
핵심 통찰 요약
by Tushar D. Ni... 게시일 www.nature.com 03-27-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07233-2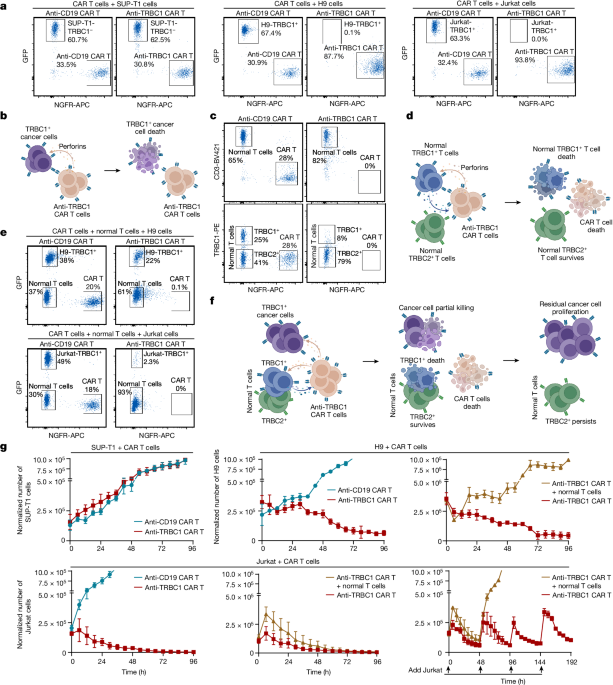
더 깊은 질문
How can the challenges faced in the first-in-human clinical trial of anti-TRBC1 CAR T cells be addressed effectively
In order to effectively address the challenges faced in the first-in-human clinical trial of anti-TRBC1 CAR T cells, several strategies can be implemented. Firstly, optimizing the design of the CAR T cells to enhance their persistence and anti-tumor activity is crucial. This can involve incorporating co-stimulatory domains, such as 4-1BB or CD28, to improve CAR T cell function and longevity. Additionally, utilizing gene editing techniques like CRISPR/Cas9 to disrupt inhibitory pathways in CAR T cells can enhance their resistance to immune-mediated killing. Moreover, implementing strategies to mitigate the immune response against CAR T cells, such as using immunosuppressive agents or engineering CAR T cells to evade immune recognition, can help improve their efficacy and durability in patients with T cell cancers.
What are the potential implications of developing antibody-drug conjugates for treating other types of cancers
The development of antibody-drug conjugates for treating other types of cancers holds significant potential implications for improving therapeutic outcomes. By targeting specific antigens expressed on cancer cells, antibody-drug conjugates can deliver potent cytotoxic agents directly to tumor cells while sparing normal tissues, thereby reducing systemic toxicity and enhancing treatment efficacy. This targeted approach can lead to higher response rates and improved patient outcomes compared to traditional chemotherapy. Additionally, antibody-drug conjugates can overcome resistance mechanisms observed with conventional therapies, offering a promising strategy for treating refractory or relapsed cancers. The versatility of antibody-drug conjugates in combining different antibodies and cytotoxic payloads allows for personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patient profiles, further enhancing the precision and effectiveness of cancer therapy.
How can the concept of preserving healthy T cells while targeting cancerous T cells be applied to other cancer treatments
The concept of preserving healthy T cells while targeting cancerous T cells can be applied to other cancer treatments by leveraging innovative immunotherapeutic approaches. For instance, in the context of solid tumors, developing bispecific antibodies that simultaneously engage tumor-specific antigens and immune checkpoint molecules can redirect cytotoxic T cells to selectively eliminate cancer cells while sparing normal tissues. This approach can enhance the anti-tumor immune response and minimize off-target toxicities associated with conventional therapies. Furthermore, utilizing adoptive cell therapies, such as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or natural killer cells, engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors specific to tumor antigens, can enable precise targeting of malignant cells while preserving the function of non-malignant immune cells. By harnessing the principles of selective tumor targeting and immune cell preservation, novel cancer treatments can be designed to achieve durable responses and improved clinical outcomes for patients across a broad spectrum of malignancies.
0
