Insights from Aerial Measurements of US Oil and Gas Emissions
Główne pojęcia
The author highlights the significant discrepancy between official estimates and actual methane emissions from oil and gas systems in the USA, emphasizing the importance of integrating aerial measurements for accurate quantification.
Streszczenie
Aerial surveys reveal substantial methane emissions not accounted for in official estimates, with regional inventories showing a range from 0.75% to 9.63% of production. Well sites and midstream facilities are identified as major contributors, with emissions representing significant economic and social costs. Continuous remote-sensing surveys are proposed for effective mitigation strategies and technology assessment.
Dostosuj podsumowanie
Przepisz z AI
Generuj cytaty
Przetłumacz źródło
Na inny język
Generuj mapę myśli
z treści źródłowej
Odwiedź źródło
www.nature.com
US oil and gas system emissions from nearly one million aerial site measurements - Nature
Statystyki
Total estimated emissions range from 0.75% to 9.63% of covered natural gas production.
Only 0.05–1.66% of well sites contribute the majority of well site emissions in most surveys.
Ancillary midstream facilities contribute 18–57% of estimated regional emissions.
The emissions represent an annual loss of roughly US$1 billion in commercial gas value and a US$9.3 billion annual social cost.
Cytaty
"Repeated, comprehensive, regional remote-sensing surveys offer a path to detect these low-frequency, high-consequence emissions for rapid mitigation."
"Well sites and midstream facilities are identified as major contributors to methane emissions."
Kluczowe wnioski z
by Evan D. Sher... o www.nature.com 03-13-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07117-5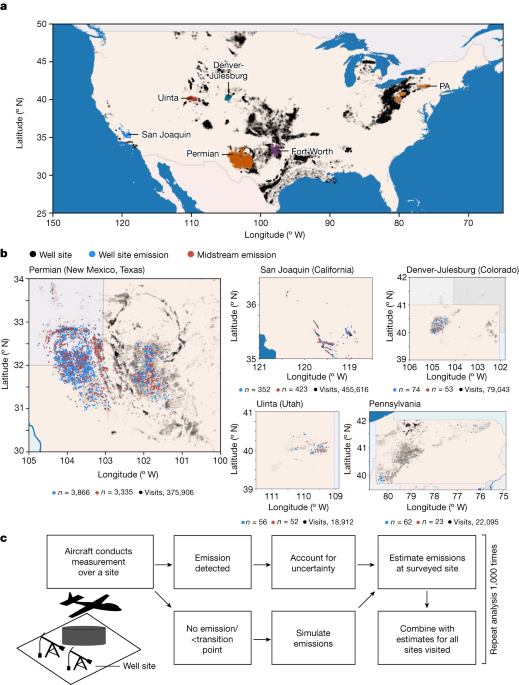
Głębsze pytania
How can the findings impact policy decisions regarding oil and gas regulations
The findings from the aerial site measurements of oil and gas system emissions can significantly impact policy decisions regarding oil and gas regulations. With the revelation that actual methane emissions are much higher than previously estimated, policymakers may be compelled to implement stricter regulations on the industry to reduce these emissions. This could involve setting more stringent emission limits, increasing monitoring requirements, or even imposing penalties for non-compliance. Additionally, policymakers may allocate more resources towards developing and enforcing regulations that target specific sources of methane emissions identified through these aerial surveys.
What potential challenges might arise in implementing rapid mitigation strategies based on these aerial measurements
Implementing rapid mitigation strategies based on these aerial measurements may face several potential challenges. One major challenge is resistance from the oil and gas industry itself, which may push back against new regulations or increased monitoring requirements that could impact their operations and profitability. Another challenge is the cost associated with implementing mitigation measures at a large scale across multiple regions. Rapidly reducing methane emissions would require significant investments in technology, infrastructure upgrades, and workforce training.
Furthermore, coordinating efforts among various stakeholders such as government agencies, industry players, environmental groups, and local communities can also pose a challenge in implementing effective mitigation strategies quickly. Balancing economic interests with environmental concerns while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards adds another layer of complexity to this process.
How can advancements in technology aid in more accurate quantification of methane emissions
Advancements in technology play a crucial role in aiding more accurate quantification of methane emissions from oil and gas systems. For instance, the use of remote sensing technologies like drones equipped with specialized sensors can provide real-time data on methane leaks from well sites or pipelines. These technological advancements enable continuous monitoring over large areas without relying solely on periodic ground-based inspections.
Additionally, machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected from aerial surveys to identify patterns and trends in methane emissions accurately pinpointing high-emission sources for targeted mitigation efforts. Integration of satellite imagery with advanced analytics tools further enhances our ability to track changes in emission levels over time across different regions.
By leveraging cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices for sensor networks, blockchain for transparent data sharing among stakeholders - we can improve our understanding of methane emissions dynamics within the oil and gas sector leading to more effective mitigation strategies tailored to specific regional needs.
0
