Climate Change Impact on Arbovirus Spread
The World Health Organization (WHO) raises concerns about the surge in arbovirus cases globally, attributing the spread to climate change. In Brazil, dengue cases have led to a record number of deaths, with southern regions affected. Dr. André Siqueira highlights the challenges faced by states unaccustomed to handling arbovirus outbreaks. WHO officials express alarm over the Americas' arbovirus situation, emphasizing the lack of immunity and healthcare system preparedness. Prompt identification of high-risk patients is crucial due to the absence of specific treatments for arboviral diseases. Climate change facilitates mosquito vector spread, impacting regions like South America and Europe. Urbanization, sanitation issues, and increased travel post-COVID-19 contribute to arbovirus proliferation globally. The WHO alerts on rising chikungunya cases worldwide, emphasizing the disease's complexity and impact. Zika, though fewer in cases, remains a concern due to associated complications. Countries are urged to enhance efforts in combating arboviruses, with the WHO committed to providing support.
Dostosuj podsumowanie
Przepisz z AI
Generuj cytaty
Przetłumacz źródło
Na inny język
Generuj mapę myśli
z treści źródłowej
Odwiedź źródło
www.medscape.com
Climate Change May Promote the Global Spread of Arboviruses
Kluczowe wnioski z
by Giuliana Mir... o www.medscape.com 04-28-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/991352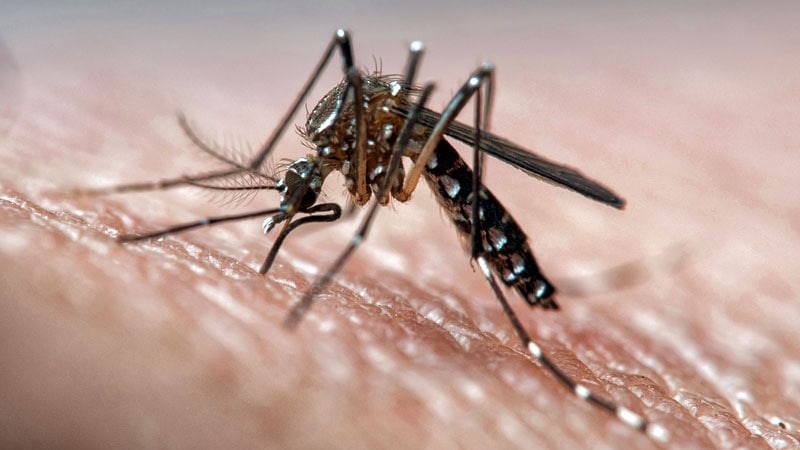
Głębsze pytania
