Hope Emerges for Patients With Rare Skin Disorder: Advances in Treatment and Therapies
Główne pojęcia
Better understanding and new therapies are improving outcomes for patients with primary cutaneous amyloidosis.
Streszczenie
The article discusses the advancements in treating primary cutaneous amyloidosis (PCA) presented by Dr. Jordan P. Talia at the Mount Sinai Winter Symposium. It highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis, categorization, and new treatment options for PCA, focusing on macular amyloidosis (MA), lichen amyloidosis (LA), and nodular amyloidosis (NA). The identification of genetic mutations in some families with PCA, along with successful case studies using monoclonal antibodies and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, suggests a promising new framework for treating the disorder.
Key Highlights:
PCA affects fewer than 50,000 people in the United States.
Accurate diagnosis and categorization are crucial for effective treatment.
Standard-of-care treatments have shown limited efficacy due to not targeting disease-generating genes.
Genetic mutations in the OSMR and IL31RA genes have been identified in some PCA patients.
Immunohistochemistry analysis revealed increased expression of OSMR beta and IL-31RA in patients with localized amyloidosis.
Case studies showed successful treatment with monoclonal antibodies and JAK inhibitors.
Potential genetic targets for MA and LA treatments are being explored.
Further research is needed on topical JAK inhibitors, dupilumab, tralokinumab, lebrikizumab, nemolizumab, and vixarelimab for MA and LA patients.
Hope Emerges for Patients With Rare Skin Disorder
Statystyki
PCA affects fewer than 50,000 people in the United States.
Mutations in the OSMR gene and the IL31RA gene have been identified in some families with PCA.
Immunohistochemistry analysis revealed increased expression of OSMR beta and IL-31RA in patients with localized amyloidosis.
Cytaty
"In the past, there were not a lot of good options for treating many depositional skin disorders but a new framework for thinking about and treating these diseases is emerging."
"These findings support further research in these treatments for patients with MA and LA."
Kluczowe wnioski z
by Myles Starr o www.medscape.com 12-05-2023
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/hope-emerges-patients-rare-skin-disorder-2023a1000udm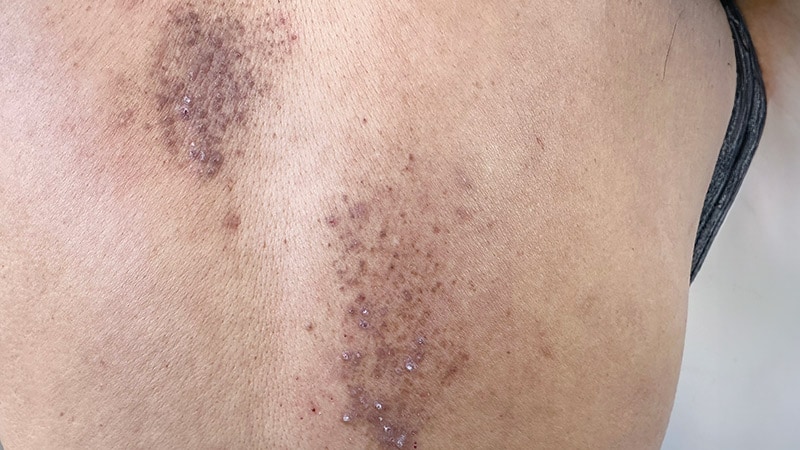
Głębsze pytania
How can the identification of genetic mutations in PCA patients impact future treatment approaches?
The identification of genetic mutations in PCA patients can significantly impact future treatment approaches by providing specific targets for therapy. Mutations in genes like OSMR and IL31RA have been linked to PCA, offering potential genetic targets for treatment. Understanding these mutations can lead to the development of targeted therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, which have shown promise in treating PCA. By targeting the underlying genetic causes of the disease, these treatments can be more effective and tailored to individual patients, improving outcomes and potentially leading to more personalized medicine approaches in the future.
What challenges might arise in implementing the new framework for treating PCA in clinical practice?
Implementing the new framework for treating PCA in clinical practice may face several challenges. One significant challenge is the availability and accessibility of these novel treatments. While advancements in therapies like JAK inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies show promise, they may not be widely available or affordable for all patients. Additionally, there may be challenges in accurately diagnosing and categorizing PCA, as the disease can present in different forms and may be misdiagnosed or overlooked. Furthermore, integrating genetic testing and personalized medicine approaches into routine clinical practice can be complex and may require specialized expertise and resources. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial to ensuring that patients with PCA can benefit from the latest advancements in treatment.
How can advancements in treating rare skin disorders like PCA contribute to broader dermatological research and patient care?
Advancements in treating rare skin disorders like PCA can have a significant impact on broader dermatological research and patient care. By studying rare diseases like PCA, researchers can uncover novel insights into disease pathology, genetic mechanisms, and treatment approaches that may have broader implications for other skin disorders. For example, the identification of genetic mutations in PCA patients not only informs treatment for PCA but also sheds light on potential genetic targets for other skin conditions. Additionally, successful treatments developed for rare skin disorders can serve as a model for personalized medicine approaches in dermatology, leading to more tailored and effective therapies for a wide range of skin conditions. Overall, advancements in treating rare skin disorders contribute to a deeper understanding of dermatological diseases, driving innovation and improving patient care across the field.
0
