Promising Antibody Therapy Shows Potential to Revolutionize Heart Failure Treatment
Conceitos essenciais
A therapeutic antibody has the potential to significantly alleviate the burden of heart failure and cardiovascular disease.
Resumo
The article discusses a promising new treatment for heart failure, a widespread condition where the heart is unable to efficiently pump blood throughout the body. The researchers describe an antibody therapy that could be a game-changer in addressing this major health challenge.
The key highlights are:
- Heart failure is a common and serious condition where the heart cannot effectively circulate blood.
- The researchers have developed a therapeutic antibody that shows potential to greatly reduce the burden of heart failure and cardiovascular disease.
- This novel antibody therapy could represent a significant advancement in the treatment of heart failure, which affects millions of people worldwide.
- The article suggests this therapy could be a transformative development in the field of cardiovascular medicine.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
Long-lasting heart-failure treatment could be a game-changer
Estatísticas
Heart failure is a widespread condition.
The therapeutic antibody has the potential to greatly reduce the burden of heart failure and cardiovascular disease.
Citações
"Heart failure is a widespread condition in which the heart can no longer efficiently pump blood around the body."
"Dunn et al.1 describe a therapeutic antibody with the potential to greatly reduce the burden of heart failure and cardiovascular disease."
Principais Insights Extraídos De
by John C. Burn... às www.nature.com 09-11-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-02660-7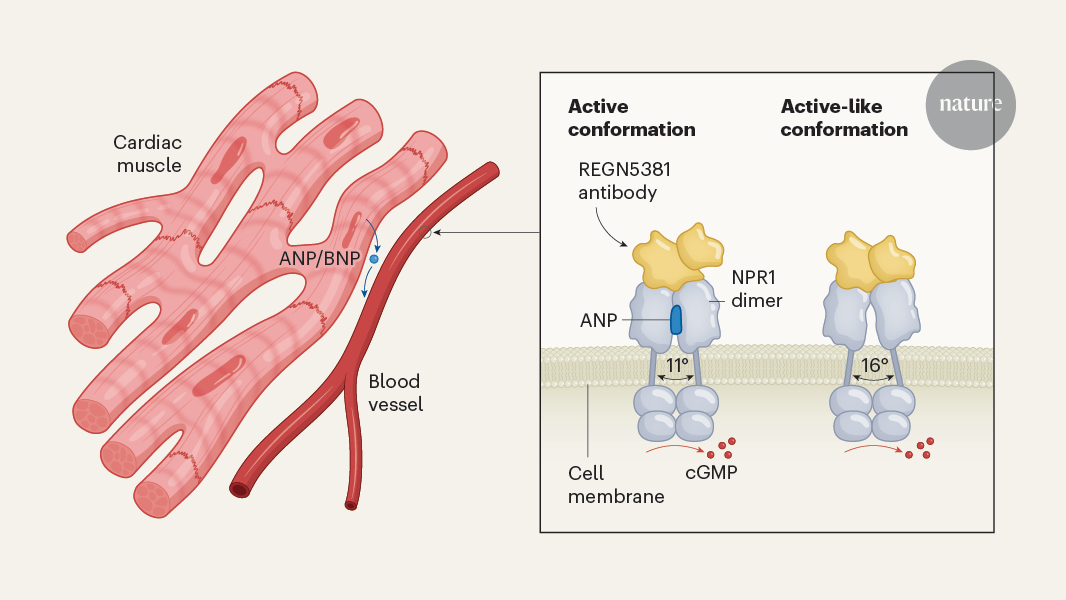
Perguntas Mais Profundas
What are the specific mechanisms by which this antibody therapy could improve heart function and cardiovascular health?
The therapeutic antibody described by Dunn et al. has the potential to enhance heart function and cardiovascular health through several specific mechanisms. Firstly, it may target and neutralize pathological factors that contribute to heart failure, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines or neurohormonal mediators like angiotensin II. By inhibiting these factors, the antibody could reduce inflammation and fibrosis in cardiac tissues, leading to improved myocardial function and reduced remodeling of the heart.
Secondly, the antibody may enhance the contractility of cardiac muscle cells by modulating calcium signaling pathways. This could lead to more effective pumping action of the heart, thereby improving cardiac output and alleviating symptoms of heart failure. Additionally, the therapy might promote angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which is crucial for supplying oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, especially in ischemic conditions.
Lastly, the antibody could potentially improve endothelial function, which is often compromised in heart failure patients. By restoring normal endothelial activity, the therapy may enhance vascular tone and reduce the risk of thrombotic events, further supporting cardiovascular health.
What are the potential limitations or challenges in developing and implementing this novel treatment approach?
Despite the promising nature of this therapeutic antibody, several limitations and challenges could hinder its development and implementation. One significant challenge is the complexity of heart failure as a multifactorial disease. The heterogeneity of heart failure patients, including variations in underlying causes, comorbidities, and responses to treatment, may complicate the identification of the most suitable patient population for this therapy.
Additionally, the development of monoclonal antibodies can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, requiring extensive preclinical and clinical testing to establish safety, efficacy, and optimal dosing regimens. There is also the potential for adverse effects, such as immune reactions or off-target effects, which could limit the therapeutic window of the antibody.
Moreover, the cost of antibody therapies can be prohibitively high, raising concerns about accessibility and affordability for patients, particularly in public health systems. Ensuring that this treatment is available to a broad population will be a critical challenge in its implementation.
How could this breakthrough in heart failure treatment impact the broader field of cardiovascular medicine and public health?
The introduction of a long-lasting therapeutic antibody for heart failure could have profound implications for the broader field of cardiovascular medicine and public health. If successful, this treatment could significantly reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with heart failure, which is a leading cause of hospitalization and healthcare expenditure worldwide.
By improving heart function and quality of life for patients, this therapy could decrease the burden on healthcare systems, leading to lower hospitalization rates and reduced healthcare costs. Furthermore, it could shift the focus of cardiovascular treatment from merely managing symptoms to addressing the underlying pathophysiology of heart failure, potentially leading to more effective long-term outcomes.
In a public health context, the availability of such a treatment could encourage earlier intervention and better management of cardiovascular risk factors, ultimately contributing to a decline in the prevalence of heart failure. This breakthrough could also stimulate further research into novel therapeutic approaches for other cardiovascular diseases, fostering innovation and collaboration within the field. Overall, the successful implementation of this antibody therapy could represent a significant advancement in the fight against cardiovascular disease, improving health outcomes on a global scale.
0
