Conceitos essenciais
Neuroscientists explore how insect brains convert direction into goal-oriented steering.
Resumo
Animals possess a remarkable ability to navigate, relying on specialized brain centers like the hippocampus in vertebrates and the central complex in insects. Neuroscientists are delving into how these neural circuits help animals build internal maps and orient themselves towards goals. Recent studies by Mussells Pires et al. and Westeinde et al. shed light on the intricate mechanisms behind insect brain navigation.
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
A neural circuit for navigation keeps flies on target
Estatísticas
"Writing in Nature, Mussells Pires et al.1 and Westeinde et al.2 reveal the detailed mechanisms by which the insect brain converts a map-like representation of direction into goal-oriented steering."
Citações
Principais Insights Extraídos De
by Katherine Na... às www.nature.com 02-07-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-00230-5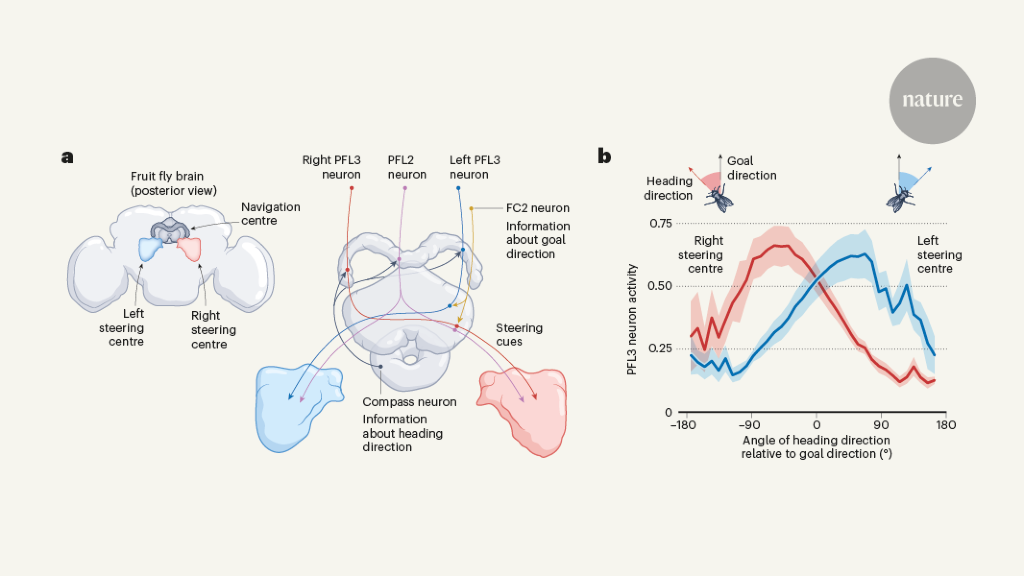
Perguntas Mais Profundas
How do these findings impact our understanding of human navigation systems?
The findings regarding the neural circuit for navigation in insects provide valuable insights into how organisms, including humans, navigate their surroundings. By understanding the detailed mechanisms by which insects convert map-like representations of direction into goal-oriented steering, we can draw parallels to the human brain's navigation centers like the hippocampus. This knowledge can deepen our comprehension of how humans build internal maps and compasses to orient themselves towards goals or desired locations. Studying insect navigation sheds light on fundamental principles that may be conserved across species, offering a comparative perspective that enriches our understanding of human navigation systems.
What challenges might arise when applying insights from insect navigation to artificial intelligence development?
While insights from insect navigation can offer innovative solutions for artificial intelligence (AI) development, several challenges may arise during implementation. One significant challenge is scaling up from simple insect brains to complex AI systems designed for diverse tasks. Insects have evolved efficient neural circuits tailored for specific behaviors, but replicating this complexity in AI models requires overcoming scalability issues and ensuring adaptability across different environments. Additionally, translating biological principles into computational algorithms poses challenges in terms of robustness, generalization, and real-time processing capabilities. Balancing biological inspiration with practical applicability in AI development demands interdisciplinary collaboration and creative problem-solving to address these challenges effectively.
How can studying insect navigation inspire advancements in robotics?
Studying insect navigation serves as a wellspring of inspiration for advancements in robotics by offering novel strategies for autonomous movement and spatial awareness. Insights into how insects utilize neural circuits to navigate complex environments can inform the design of robotic systems capable of adaptive locomotion and goal-directed behavior. By mimicking key features such as decentralized control mechanisms or sensor fusion techniques observed in insects, roboticists can enhance robot autonomy and efficiency in navigating unstructured terrains or dynamic settings. Furthermore, studying insect-inspired algorithms like swarm intelligence or path integration enables the development of collaborative robotic systems that exhibit emergent behaviors similar to social insects' collective decision-making processes. Overall, leveraging lessons from insect navigation opens new avenues for enhancing robotic capabilities through bio-inspired approaches that prioritize agility, robustness, and energy efficiency.
0
