Inhibiting Cell Death Pathway Reduces Lung Damage and Inflammation in Severe Influenza Infections
Temel Kavramlar
Inhibiting the cell death pathway of necroptosis can reduce the excessive inflammatory response and mortality in severe influenza infections.
Özet
The article discusses the importance of understanding and addressing the next influenza pandemic, which has the potential to be highly lethal, especially for younger, seemingly healthy adults. The authors highlight a study by Gautam et al. that demonstrates how inhibiting a specific cell death pathway called necroptosis can mitigate the severe inflammatory response and reduce mortality in an animal model of severe influenza infection.
The key insights from the article are:
Influenza pandemics have killed millions in the past and could do so again, with some strains proving particularly lethal to younger, healthy adults.
This may be due to the strong inflammatory response provoked by the virus in this group.
The study by Gautam et al. shows that inhibiting the cell death pathway of necroptosis can reduce the excessive inflammatory response and substantially lower mortality in an animal model of severe influenza infection.
Targeting this cell death pathway could be a promising therapeutic approach to improve outcomes in severe influenza cases.
Blocking cell death limits lung damage and inflammation from influenza
İstatistikler
Influenza pandemics have killed millions in the past.
Some influenza strains have proved to be particularly lethal to younger, ostensibly healthy adults.
Alıntılar
"If there is one lesson to be learnt from the pandemic, it is that we need to be better prepared for the next one."
"Influenza pandemics have killed millions in the past and could do so again."
Önemli Bilgiler Şuradan Elde Edildi
by Nishma Gupta : www.nature.com 04-10-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-00910-2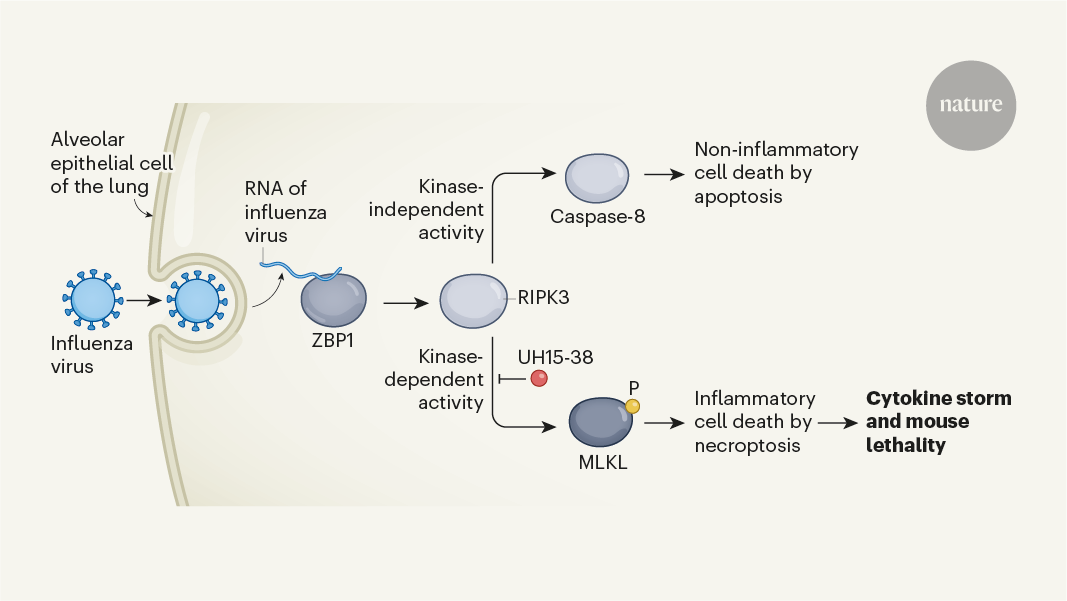
Daha Derin Sorular
How can we better prepare for the next influenza pandemic, beyond targeting the cell death pathway of necroptosis?
To better prepare for the next influenza pandemic, beyond targeting the cell death pathway of necroptosis, several strategies can be implemented. Firstly, enhancing global surveillance systems to detect emerging influenza strains early on is crucial. This includes improving coordination between countries and sharing data promptly. Additionally, investing in the development of universal influenza vaccines that provide broad protection against multiple strains can be beneficial. Strengthening healthcare infrastructure to handle a surge in cases, ensuring an adequate supply of antiviral medications, and promoting public awareness campaigns on preventive measures like vaccination and hygiene practices are also essential steps in preparedness.
What other host immune pathways or viral mechanisms could be targeted to mitigate the excessive inflammatory response in severe influenza infections?
Apart from targeting the cell death pathway of necroptosis, other host immune pathways or viral mechanisms that could be targeted to mitigate the excessive inflammatory response in severe influenza infections include the NLRP3 inflammasome, which is involved in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By modulating the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, it may be possible to reduce the inflammatory damage caused by influenza. Additionally, targeting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which plays a role in regulating immune responses, could be another approach to dampen the excessive inflammation associated with severe influenza infections.
What are the potential long-term consequences of inhibiting necroptosis, and how can we ensure the safety and efficacy of this approach in clinical settings?
Inhibiting necroptosis to reduce inflammation in severe influenza infections may have potential long-term consequences, such as impairing the immune system's ability to clear viral infections efficiently. This could lead to prolonged viral shedding and increased susceptibility to secondary infections. To ensure the safety and efficacy of this approach in clinical settings, thorough preclinical studies are essential to understand the impact of necroptosis inhibition on overall immune function. Clinical trials should be conducted to assess the treatment's effectiveness and monitor for any adverse effects. Close monitoring of patients receiving necroptosis inhibitors, along with personalized treatment plans based on individual immune responses, can help optimize the balance between reducing inflammation and maintaining antiviral immunity.
0
