Challenges in Predicting RA Treatment Responses
核心概念
Precision medicine in predicting treatment responses for rheumatoid arthritis remains challenging due to the complexity of the disease.
摘要
The content discusses the challenges researchers face in predicting treatment responses for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) through synovial tissue biopsy analysis. Here is a breakdown of the key points:
Predicting Treatment Responses:
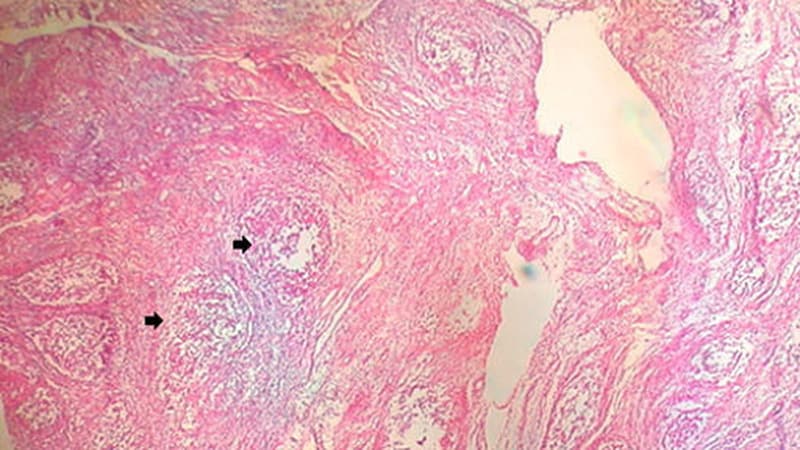
Synovial tissue biopsy analysis is unreliable in predicting responses to etanercept, tocilizumab, or rituximab.
Current RA treatments involve trial and error due to the lack of reliable predictive methods.
The STRAP Studies:
Combined data from two clinical trials, STRAP and STRAP-EU, to analyze treatment responses in biologic-naive RA patients.
No significant differences in treatment responses between rituximab, etanercept, and tocilizumab groups based on synovial B-cell classification.
Molecular-Level Analyses:
Histology is insufficient to predict treatment responses accurately.
Advanced molecular analyses, such as spatial transcriptomics, are crucial for understanding RA heterogeneity.
Future Directions:
A larger study incorporating various patient information sources is essential for advancing precision treatment for RA.
Synovial tissue analysis remains crucial for achieving precision medicine in RA.
Trial Shows Precision Medicine in RA 'Remains Elusive'
統計資料
"In total, researchers recruited 223 biologic-naive adult patients from 26 universities in the UK and Europe."
"Around 60% of patients achieved the primary endpoint of at least 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria."
引述
"Precision medicine, therefore, remains elusive."
"The tissue is the golden ticket, but it's how you analyze it."
"Precision medicine for RA is close. We still have to get the numbers."
深入探究
How can advanced molecular analyses improve the prediction of treatment responses in RA?
Advanced molecular analyses, such as spatial transcriptomics, can significantly enhance the prediction of treatment responses in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by providing a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying disease mechanisms at a molecular level. By analyzing gene expression in individual cells within synovial tissue samples, researchers can identify specific molecular pathways and biomarkers associated with treatment response. This detailed molecular information allows for a more personalized approach to treatment selection, as clinicians can tailor therapies based on the unique molecular profile of each patient. Additionally, spatial transcriptomics enables the mapping of gene activity within tissues, providing insights into the spatial distribution of molecular changes that may influence treatment outcomes. Overall, advanced molecular analyses offer a more precise and targeted way to predict treatment responses in RA, moving towards the goal of precision medicine in rheumatology.
What are the ethical implications of trial-and-error treatment approaches in RA management?
The trial-and-error treatment approaches commonly used in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) management raise several ethical considerations. One key ethical implication is the potential for patient harm, as individuals may experience prolonged disease activity, unnecessary side effects, and delays in achieving optimal disease control while undergoing multiple treatment trials. This approach can also lead to increased healthcare costs, as patients may receive ineffective treatments before finding a suitable therapy. Furthermore, the lack of reliable predictive tools in RA treatment decision-making may result in disparities in care, with some patients experiencing better outcomes due to chance rather than personalized treatment selection based on scientific evidence. Ethical concerns also arise regarding informed consent, as patients may not fully understand the uncertainties and risks associated with trial-and-error approaches. Overall, the ethical implications of trial-and-error treatment in RA underscore the importance of advancing precision medicine to improve patient outcomes and minimize potential harm.
How can the integration of spatial transcriptomics revolutionize precision medicine in various medical fields?
The integration of spatial transcriptomics has the potential to revolutionize precision medicine across various medical fields by providing a deeper understanding of disease processes at a cellular and spatial level. By mapping gene expression patterns within tissues, spatial transcriptomics allows researchers to identify specific cell types, interactions, and molecular pathways involved in disease pathogenesis. This spatially resolved molecular information can lead to the discovery of novel biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and personalized treatment strategies tailored to individual patients. In oncology, spatial transcriptomics can enhance tumor characterization, predict treatment responses, and guide precision oncology interventions. In neurology, this technology can elucidate the molecular basis of neurological disorders and facilitate the development of targeted therapies. Overall, the integration of spatial transcriptomics holds great promise for advancing precision medicine by enabling a more detailed and spatially informed understanding of disease mechanisms across diverse medical fields.
0
