Comprehensive Sequencing and Comparative Analysis of Sex Chromosomes in Apes
Core Concepts
Ape sex chromosomes exhibit dynamic evolution, with the Y chromosome showing greater variation in size, structure, and gene content compared to the more stable X chromosome.
Abstract
The article presents a comprehensive analysis of the sex chromosomes of five great ape species (bonobo, chimpanzee, western lowland gorilla, Bornean orangutan, and Sumatran orangutan) and one lesser ape species (siamang gibbon). Using the telomere-to-telomere (T2T) methodology, the researchers were able to produce gapless assemblies of the X and Y chromosomes for these species, allowing them to unravel the intricacies of sex chromosome evolution in apes.
The key findings are:
Compared to the X chromosomes, the ape Y chromosomes exhibit greater variation in size and have lower alignability and higher levels of structural rearrangements, due to the accumulation of lineage-specific ampliconic regions, palindromes, transposable elements, and satellites.
Many Y chromosome genes expand into multi-copy families, and some evolve under purifying selection, indicating dynamic evolution of the Y chromosome.
In contrast, the X chromosome is more stable across ape species.
Mapping short-read sequencing data to the new reference assemblies revealed patterns of diversity and selection on the sex chromosomes of more than 100 individual great apes.
The authors emphasize that these high-quality reference assemblies will inform studies on human evolution and the conservation genetics of endangered non-human ape species.
The complete sequence and comparative analysis of ape sex chromosomes - Nature
Stats
The Y chromosome exhibits greater variation in size among ape species compared to the X chromosome.
The ape Y chromosomes have lower alignability and higher levels of structural rearrangements compared to the X chromosomes.
Many Y chromosome genes expand into multi-copy families, and some evolve under purifying selection.
Quotes
"Compared with the X chromosomes, the ape Y chromosomes vary greatly in size and have low alignability and high levels of structural rearrangements—owing to the accumulation of lineage-specific ampliconic regions, palindromes, transposable elements and satellites."
"Many Y chromosome genes expand in multi-copy families and some evolve under purifying selection."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Kateryna D. ... at www.nature.com 05-29-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07473-2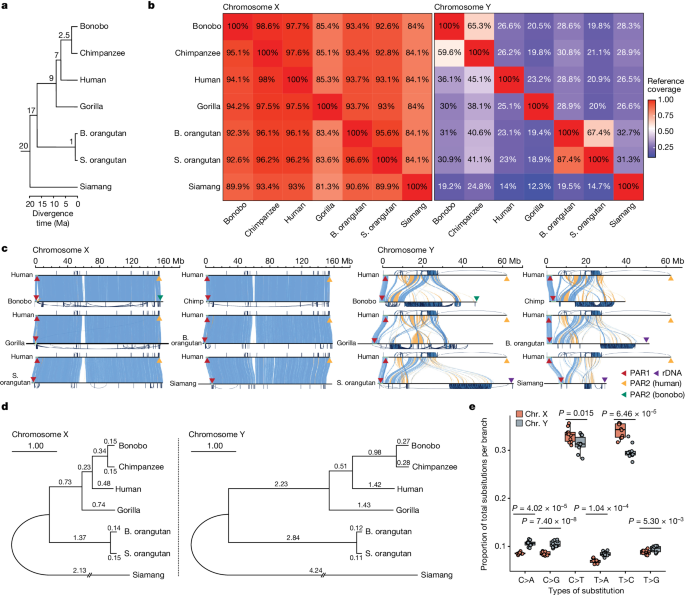
Deeper Inquiries
How do the differences in sex chromosome evolution between apes and other mammals contribute to their unique reproductive and cognitive characteristics?
The differences in sex chromosome evolution between apes and other mammals play a significant role in shaping their unique reproductive and cognitive characteristics. In apes, the Y chromosome exhibits dynamic evolution characterized by variations in size, low alignability, and high levels of structural rearrangements. This dynamic evolution is attributed to the accumulation of lineage-specific ampliconic regions, palindromes, transposable elements, and satellites on the Y chromosome. These structural features contribute to the diversification of Y chromosome genes, with many expanding in multi-copy families and some evolving under purifying selection. On the other hand, the X chromosome in apes is more stable compared to the Y chromosome. The X chromosome is vital for reproduction and cognition, and its stability may contribute to the maintenance of essential genes and functions related to these processes. Therefore, the differences in sex chromosome evolution between apes and other mammals likely underlie the unique reproductive and cognitive characteristics observed in apes.
What are the potential implications of the dynamic Y chromosome evolution for the conservation of endangered ape species?
The dynamic evolution of the Y chromosome in apes has several potential implications for the conservation of endangered ape species. The accumulation of lineage-specific ampliconic regions, palindromes, transposable elements, and satellites on the Y chromosome contributes to its structural complexity and genetic diversity. This genetic diversity on the Y chromosome may play a crucial role in the adaptation and survival of ape populations facing environmental challenges and threats. Understanding the dynamic evolution of the Y chromosome in endangered ape species can provide valuable insights into their genetic diversity, population dynamics, and evolutionary history. Conservation efforts can benefit from this knowledge by implementing strategies that preserve the genetic variability present on the Y chromosome, thereby enhancing the long-term viability and resilience of endangered ape populations.
How can the insights from ape sex chromosome analysis be leveraged to better understand the evolution of sex chromosomes in other primates and vertebrates?
Insights from ape sex chromosome analysis can be leveraged to better understand the evolution of sex chromosomes in other primates and vertebrates by providing comparative data and evolutionary context. The detailed analysis of ape sex chromosomes, including the X and Y chromosomes, offers a comprehensive view of the structural and functional differences between these chromosomes in different ape species. By comparing the evolution of sex chromosomes across apes, researchers can identify common patterns, lineage-specific changes, and evolutionary dynamics that may be shared with other primates and vertebrates. This comparative approach can help elucidate the mechanisms driving sex chromosome evolution, such as gene duplication, purifying selection, and structural rearrangements, and how these processes contribute to species-specific traits and adaptations. Leveraging the insights from ape sex chromosome analysis can therefore enhance our understanding of sex chromosome evolution in a broader evolutionary context, shedding light on the genetic mechanisms shaping reproductive biology and cognitive functions in diverse primate and vertebrate species.
0
