Spatial Positioning of Cell Nuclei Regulates Tissue Development
Core Concepts
Cell nuclei positioned at the tissue surface receive specific signals that fuel their development.
Abstract
The article discusses how the spatial positioning of cell nuclei within a tissue can influence the development of specialized tissues. The authors, Willnow and Teleman, have uncovered a developmental process that is regulated by the location of the cell nucleus relative to the tissue surface.
Tissues are composed of various cell types that must coordinate their activities in a precise manner to facilitate proper development. This requires intricate control over the timing and location of different cellular mechanisms. The researchers found that cell nuclei facing the tissue surface receive specific signals that provide them with the necessary fuel to drive their development.
This spatial regulation of cellular processes is an important factor in tissue patterning and morphogenesis. The authors suggest that the proximity of the cell nucleus to the tissue surface allows it to access critical resources or signaling cues that are not available to nuclei located deeper within the tissue. This spatial positioning of the nucleus relative to the tissue boundary appears to be a key determinant in regulating the development of specialized cell types and structures.
The findings highlight the importance of considering the spatial organization of cells within a tissue when studying developmental processes. Understanding how the physical location of a cell's nucleus can influence its behavior and fate is crucial for elucidating the complex mechanisms underlying tissue formation and homeostasis.
Nuclei facing the tissue surface get fuel for development
Stats
The development of specialized tissues relies on the intricate interplay between various cellular mechanisms.
The careful control over the timing and location of these processes is crucial for proper tissue development.
Quotes
"The development of specialized tissues relies on the intricate interplay between various cellular mechanisms, and the careful control over the timing and location of these processes."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Tanvi Kulkar... at www.nature.com 06-05-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-024-01503-9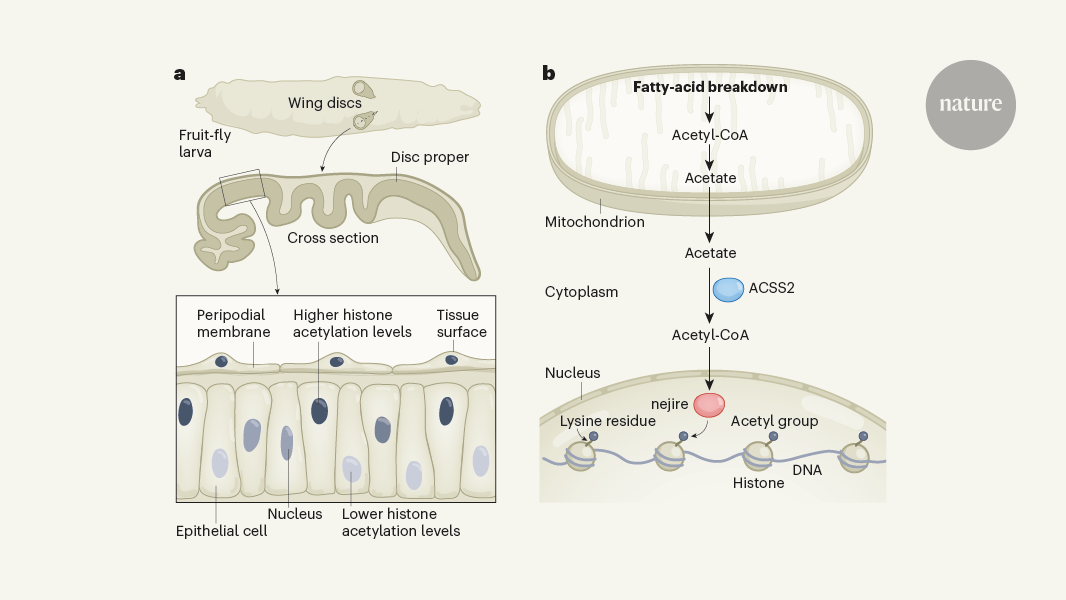
Deeper Inquiries
How might the specific signals or resources received by nuclei at the tissue surface differ from those available to nuclei located deeper within the tissue?
Nuclei located at the tissue surface are more likely to receive signals or resources that are crucial for development compared to those deeper within the tissue. This is because surface nuclei have direct access to external factors such as growth factors, nutrients, and oxygen from the surrounding environment. These external signals play a significant role in initiating and regulating cellular processes like proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis. In contrast, nuclei deeper within the tissue may have limited exposure to these external cues and rely more on signals from neighboring cells or the extracellular matrix. This difference in signal availability can lead to distinct gene expression patterns and cellular behaviors between surface and deep nuclei during tissue development.
What other factors, besides spatial positioning, might contribute to the differential regulation of cellular mechanisms during tissue development?
In addition to spatial positioning, several other factors can contribute to the regulation of cellular mechanisms during tissue development. These factors include cell-cell interactions, signaling pathways, mechanical forces, and the microenvironment. Cell-cell interactions through direct contact or paracrine signaling can influence the behavior of neighboring cells and coordinate their activities. Signaling pathways such as Wnt, Notch, and TGF-β play critical roles in determining cell fate and tissue patterning. Mechanical forces exerted by the extracellular matrix or neighboring cells can also impact cellular behavior, differentiation, and tissue morphogenesis. The microenvironment, including factors like pH, temperature, and oxygen levels, can further modulate cellular responses and gene expression patterns during tissue development.
How could the insights from this study on spatial regulation of cell nuclei be applied to regenerative medicine or tissue engineering approaches?
The insights gained from studying the spatial regulation of cell nuclei could have significant implications for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering approaches. By understanding how the positioning of nuclei influences cellular behavior and tissue development, researchers can design more effective strategies for regenerating damaged tissues or engineering artificial organs. For example, in regenerative medicine, manipulating the spatial organization of cells or nuclei within a scaffold could enhance tissue regeneration and functional recovery. In tissue engineering, optimizing the distribution of nuclei within engineered constructs could improve the maturation and functionality of the resulting tissues. Overall, leveraging the knowledge of spatial regulation of cell nuclei could lead to innovative approaches for enhancing the success and efficiency of regenerative therapies and tissue engineering applications.
0
