Core Concepts
Global warming is accelerating the melting of polar ice, leading to changes in Earth's rotation and potentially requiring adjustments to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) earlier than planned.
Abstract
The content discusses the impact of global warming on global timekeeping due to changes in Earth's rotation. It highlights how the increased melting of ice in Greenland and Antarctica has affected the angular velocity of Earth, leading to potential disruptions in UTC. The analysis shows a constant decrease in the angular velocity of Earth's liquid core since 1972, which could necessitate a negative discontinuity in UTC by 2029. This acceleration in polar ice melting due to global warming is already influencing global timekeeping systems.
- Historical link between time and Earth's rotation
- UTC complications due to leap seconds
- Impact of ice melting on Earth's angular velocity
- Prediction of future Earth orientation and UTC adjustments
- Accelerated polar ice melting due to global warming
Customize Summary
Rewrite with AI
Generate Citations
Translate Source
To Another Language
Generate MindMap
from source content
Visit Source
www.nature.com
A global timekeeping problem postponed by global warming - Nature
Stats
"Since 1972, all UTC discontinuities have required that a leap second be added."
"Removing the effect of increased ice melting shows a constant decrease in the angular velocity of Earth's liquid core."
"Extrapolating trends predicts a negative discontinuity in UTC by 2029."
Quotes
"Global warming is already affecting global timekeeping."
Key Insights Distilled From
by Duncan Carr ... at www.nature.com 03-27-2024
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07170-0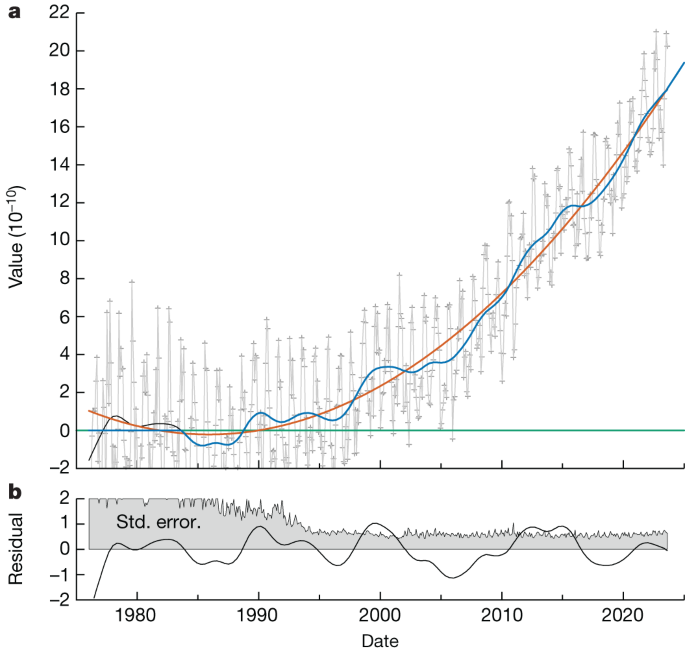
Deeper Inquiries
How can advancements in technology mitigate the challenges posed by changes in Earth's rotation?
Advancements in technology can help mitigate the challenges posed by changes in Earth's rotation by developing more sophisticated algorithms and systems for timekeeping. For instance, the use of atomic clocks, which are highly precise and stable, can provide a reliable source of time independent of Earth's rotation. By incorporating these atomic clocks into global timekeeping systems, such as the Network Time Protocol (NTP), discrepancies caused by changes in Earth's rotation can be minimized. Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can help predict and adjust for variations in Earth's rotation, ensuring the accuracy of timekeeping systems despite external factors.
What are the potential implications of adjusting UTC earlier than planned on a global scale?
Adjusting Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) earlier than planned can have significant implications on a global scale. One major implication is the need for coordination and synchronization across various sectors that rely on precise timekeeping, such as telecommunications, finance, transportation, and scientific research. Any changes to UTC would require updates to software, hardware, and systems worldwide to ensure compatibility and accuracy. Moreover, the adjustment could lead to disruptions in international communication and data exchange, potentially impacting global trade and collaboration. Additionally, there may be legal and regulatory challenges in implementing the changes, as different countries and organizations may have varying policies and procedures regarding time standards.
How can society adapt to the increasing impact of global warming on fundamental aspects of our world like timekeeping?
Society can adapt to the increasing impact of global warming on fundamental aspects of our world, such as timekeeping, by promoting sustainability and climate action. One approach is to raise awareness about the connection between environmental changes, like polar ice melting, and scientific phenomena, like Earth's rotation. Educating the public about the implications of global warming on timekeeping can foster a sense of urgency and encourage individuals and communities to take action to mitigate climate change. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources and reducing carbon emissions can help slow down the rate of global warming, potentially alleviating some of the challenges faced by timekeeping systems. Collaboration between governments, industries, and research institutions is essential to develop innovative solutions that address the intersection of global warming and timekeeping, ensuring the resilience and sustainability of our timekeeping infrastructure in the face of environmental changes.
0
